What causes HIV-related fatigue?
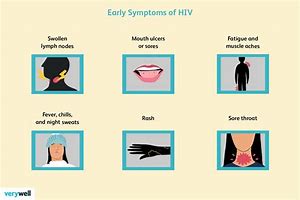
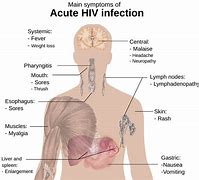
Many people who are living with HIV experience fatigue. It may be directly related to HIV or indirectly related through medications, psychological effects, or life stress. In this article, we look at the causes of HIV-related fatigue, how to overcome fatigue, and the effects HIV has on a person’s mental health. An unusual...