Vitamin A is an essential substance for the body. We can supplement vitamins through foods such as carrots, liver, egg yolks, etc. So what are the effects of vitamin A, how to use it, and does it have side effects on our body? Let’s find out through the following article.
1 What is Vitamin A?
Vitamin A is an essential nutrient for humans. Although we often think of it as a single substance, vitamin A is actually the name of a group of fat-soluble compounds, including retinol, retinal, and retinyl esters.
Vitamin A is found in many foods, in foods of animal origin vitamin A exists as retinol and retinyl esters, and in plants it exists as carotene (provitamin A). Animal liver, egg yolks, green vegetables, carrots, pumpkin, … are foods that contain a lot of vitamin A.
To use them, your body must convert the vitamin forms in food into the active forms of vitamin A, retinal acid and retinoic acid.
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin, it is stored in body tissues for use. Most of the vitamin A in your body is kept in the liver in the form of retinyl esters. (See also vitamin A products that help boost the immune system, help the body fight infections, and protect the skin from sun damage).

What is vitamin A?
2 Effects of vitamin A on the body
Vitamin A is good for the eyes and prevents macular degeneration.

Vitamin A is good for the eyes
Vitamin A is essential for vision and eye health. Retinal, the active form of vitamin A, combines with the protein opsin to form rhodopsin, a molecule needed for color vision and seeing in the dark.
It also helps protect and maintain the cornea – the outermost layer of the eye – and the conjunctiva – a thin membrane that covers the surface of your eye and the inside of your eyelids
A diet rich in vitamin A helps protect against certain eye diseases, such as age-related macular degeneration. Studies show that higher blood levels of beta-carotene, alpha-carotene, and beta-cryptoxanthin can reduce the risk of macular degeneration by up to 25%.
According to the WHO, vitamin A deficiency is the leading cause of blindness in children worldwide.
Vitamin A is good for the skin

Vitamin A is good for the skin
The skin is the organ that responds to retinoids (a form of vitamin A) and can easily absorb vitamin A when applied topically.
Vitamin A stimulates the production of new skin cells. Vitamin A deficiency can cause dry, cracked skin.
According to research on retinoids in the treatment of skin aging, retinol deficiency can also cause follicular hyperkeratosis, and cause raised papules on the skin.
Studies reported in Toxicology also show that retinol is effective in stimulating collagen production and reducing wrinkles when used topically.
Vitamin A may protect against certain cancers
Vitamin A helps fight cancer
The antioxidant properties of carotenoids (precursors of vitamin A) may help protect against certain types of cancer.
For example, a study of 10,000 adults determined that smokers with the highest blood levels of alpha-carotene and beta-cryptoxanthin had a 46% and 61% lower risk of dying from lung cancer than nonsmokers with the lowest intake of these nutrients.
Furthermore, test-tube studies have shown that retinoids can inhibit the growth of certain cancer cells, such as bladder, breast, and ovarian cancer.
Vitamin A is important for fertility and fetal development.
Vitamin A is important for fetal development.
Vitamin A is essential for both male and female reproduction as it plays a role in the development of sperm and eggs.
It is also important for the health of the placenta, the growth and maintenance of fetal tissue, and the development of the fetus.
Therefore, vitamin A is indispensable for the health of mothers and fetuses and those in the reproductive stage.
Vitamin A helps strengthen the immune system

Vitamin A helps boost the immune system
Carotene, a precursor of vitamin A, is a powerful antioxidant that helps fight free radicals that damage body cells, stimulating reactions that protect the body from bacteria and harmful factors.
Vitamin A is involved in the creation of certain cells, including B cells and T cells, which are central components in immune responses that protect against disease.
3 Recommended Dosages of Vitamin A

Vitamin A dosage
The recommended daily dose of vitamin A for normal people is 900 mcg for men and 700 mcg for women and can be fully supplemented through daily diet.
In cases of vitamin A deficiency and higher vitamin A needs, we can supplement vitamin A orally as directed by a doctor. However, it is important not to exceed the limit of 10,000 IU (3,000 mcg) for adults to prevent vitamin A toxicity.
4 Side effects and toxicity of vitamin A overdose
Because vitamin A is fat-soluble, it is stored in the body and can reach unhealthy levels if taken in excess of the recommended daily dose over a long period of time.
Taking too much vitamin A can lead to serious side effects and can even be fatal if taken in extremely high doses.
Acute vitamin A toxicity occurs over a short period of time when a very high dose of vitamin A is consumed. Although less common than chronic vitamin A toxicity, acute vitamin A toxicity is associated with more serious symptoms, including liver damage, increased intracranial pressure, and even death.
Chronic vitamin A toxicity occurs when doses are more than 10 times the recommended daily dose and are taken over a long period of time. The most common side effects of chronic vitamin A toxicity include:
- Vision disturbances
- Joint and bone pain
- Loss of appetite, nausea, and vomiting
- Sensitivity to sunlight
- Hair loss
- Headaches
- Dry skin, jaundice, itchy skin
- Liver damage
- Slow growth
5 Foods Rich in Vitamin A
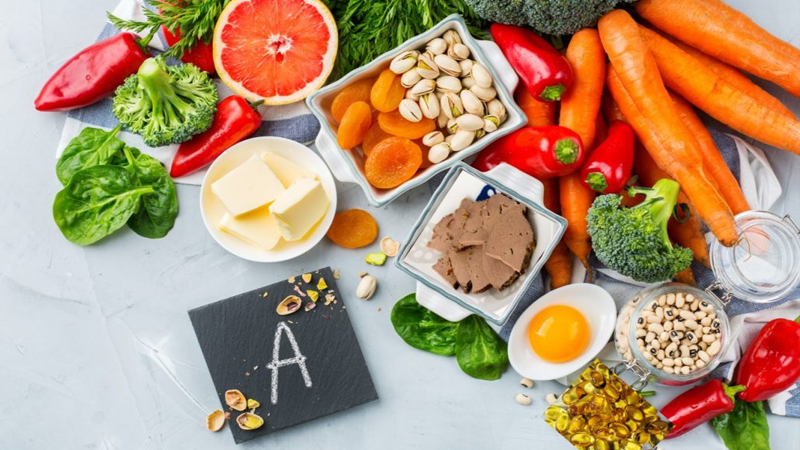

Foods rich in vitamin A
Vitamin A is found in many foods. Our bodies can be fully supplemented with vitamin A through our daily diet.
Foods of animal origin contain a lot of vitamin A such as animal liver, egg yolks, fish liver oil, etc.
For foods of plant origin, vitamin A is often found in yellow, red, or dark green vegetables such as carrots, tomatoes, broccoli, bell peppers, etc.
Through the above article, we hope you can better understand the benefits of vitamin A as well as the harmful effects it brings when overdosed. Be more careful when supplementing vitamin A and balancing your diet so as not to exceed the recommended dose of vitamin A in your daily diet.





