Zinc is an extremely necessary mineral for us, it is present in many important chemical reactions in the body. Let’s find out what effect zinc has on the body!
Overview of zinc
Zinc is present in most biochemical reactions that exist in the human body. It is the second most essential trace element for chemical reactions, second only to iron.
Zinc supports more than 300 enzymes to perform functions in the digestive, nervous, endocrine, cardiovascular systems, etc., helping cells develop and divide, and is also necessary for protein and DNA activity.
Our body absorbs zinc through the small intestine, then it is distributed throughout the body to perform metabolic reactions in functional organs.
The human body is unable to synthesize zinc itself and needs to be supplemented from external sources, through food, drinking water, and supplements.
Zinc is usually introduced into the body in the form of zinc gluconate, zinc acetate, or zinc sulfate. Although the body only needs a very small amount of zinc, the effects of zinc are really important.
This mineral is known for its many uses. Today, with modern science, the uses of zinc are increasingly being researched and clarified by scientists.
1. Strengthen the immune system
The effects of zinc on the immune system are well known. Zinc is an essential active ingredient for the function of immune cells.
When there is a zinc deficiency, immune cells do not receive signals from other organs, leading to their inability to perform their functions properly. As a result, health is weakened and susceptible to attack by external harmful agents.
When zinc is supplemented sufficiently, it will stimulate the immune system to function effectively, reducing the risk of infection. (See more zinc products that support the strengthening of the digestive system, improve the ability to absorb nutrients, and enhance the body’s resistance).
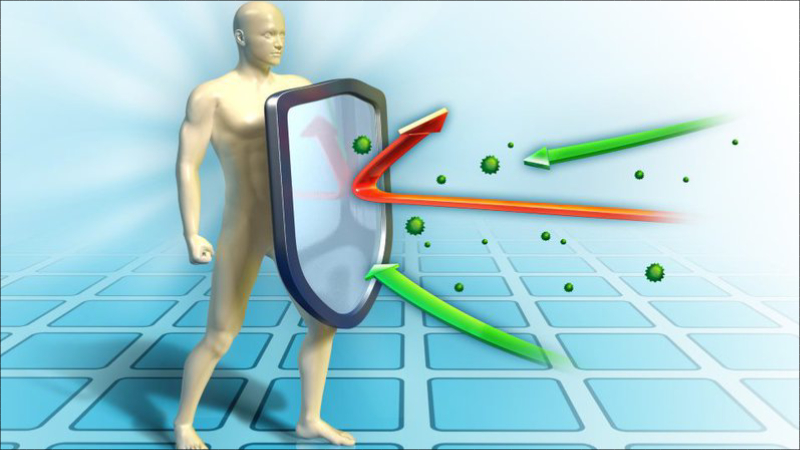
Stimulating immune cells to function effectively is one effect of zinc on the body.
2. Accelerate wound healing
Zinc plays a role in maintaining healthy skin, and is often chosen for treatment in patients with burns and skin ulcers because zinc supplementation will speed up wound healing.
A study has shown that zinc has the ability to heal wounds in diabetic patients with foot ulcers.
To achieve the best wound healing effect, in addition to using zinc, you can combine it with scar prevention products, helping wounds heal faster and limiting the appearance of unsightly scars.
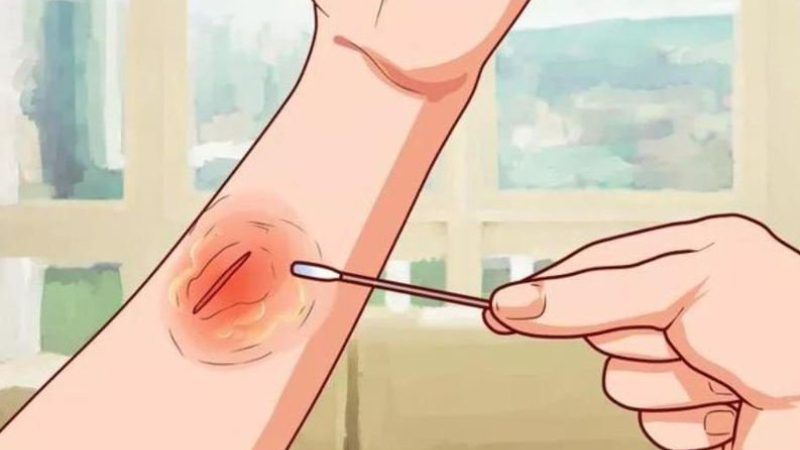
Zinc is also involved in the wound healing process.
3. Reduce the risk of some chronic, age-related diseases
An effect of zinc that many people do not know about is that zinc has the ability to reduce the risk of age-related diseases: infections, pneumonia, blurred vision due to macular degeneration (AMD), …
In a clinical trial, elderly people who took 45 mg of zinc per day reduced the rate of infection by nearly 66%.
In addition, recent studies have shown that zinc deficiency in the elderly reduces immunity, increases the rate and duration of pneumonia and increases the time of antibiotic use.
Thus, adequate zinc supplementation for the elderly is also an effective way to reduce the risk of disease.

Elderly people need to be adequately supplemented with zinc to reduce the risk of diseases of old age.
4. Protect eyesight
Zinc is also an antioxidant, helping to fight free radicals to avoid damaging cells, preventing oxidative stress. Therefore, supplementing zinc from food or functional foods can help protect the eyes, limiting the risk of vision loss.

Zinc helps prevent oxidative stress, reducing the risk of vision loss.
5. Helps treat acne
Zinc is an active ingredient used to treat acne due to its ability to reduce inflammation and inhibit the growth of P.acnes bacteria, while reducing the overactivity of the sebum glands. Patients can apply zinc products to the skin or take it orally to reduce acne.
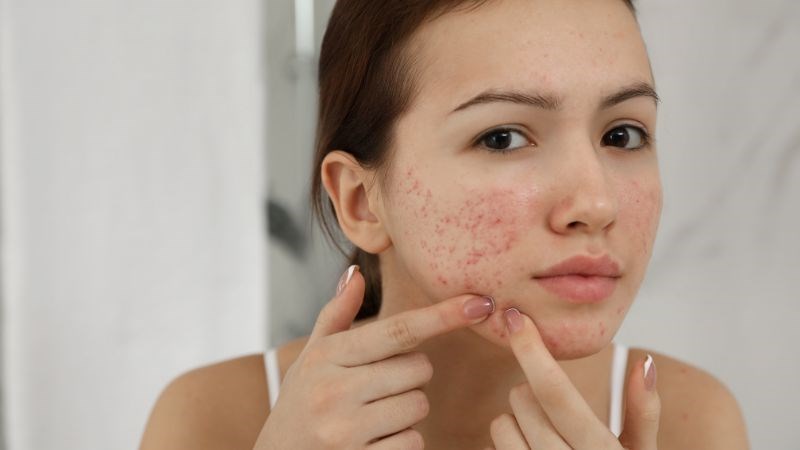

Zinc is used in the treatment of acne.
6. Support for diarrhea treatment
If diarrhea lasts too long, patients should supplement zinc, especially children. Zinc will help reduce the duration of diarrhea and promote intestinal recovery to improve diarrhea.
Zinc can help control diarrhea caused by both bacteria and viruses. For a quick and effective recovery, patients should supplement zinc and use probiotics to rebalance the beneficial bacteria in the intestines.

Zinc helps speed up intestinal recovery
7. Reduce oxidative stress
Oxidative stress is very harmful to human health, it is an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body, in the long term leading to some diseases such as diabetes, atherosclerosis, heart disease, and even cancer. In addition, oxidative stress also contributes to accelerating the aging process.
Zinc is an antioxidant, providing zinc will limit the imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants, limit oxidative stress, and protect health.
8. Reduce inflammation
This effect of zinc is due to its ability to reduce oxidation reactions and reactions that create inflammatory mediators in the human body such as: thromboxane, leukotriens and prostaglandin.
A study gave patients 45 mg of zinc gluconate per day for 6 months. The results measured high blood zinc levels, while reducing signs of inflammation in the body.
9. Preventing osteoporosis
Calcium is the most essential active ingredient for bone formation. However, for this process to take place smoothly, the presence of zinc is required. Zinc promotes bone mineralization, stimulating bone formation.
Therefore, for patients with osteoporosis or at risk of osteoporosis, doctors often prescribe calcium supplements with zinc and some other micronutrients. (See more calcium products to help prevent osteoporosis in adults, prevent rickets in children).
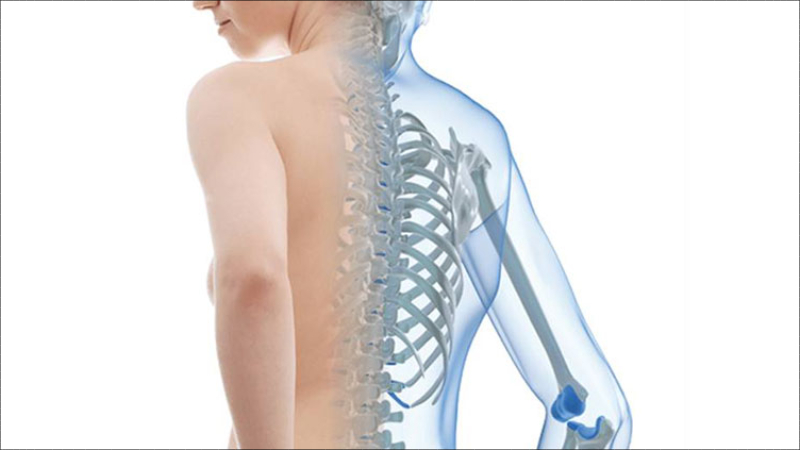
The formation of new bone cannot be without the mineral zinc.
10. Support treatment of common cold
Cold is a symptom of a disease caused by a virus. In this case, patients should take zinc to increase resistance and the immune system to help fight the virus.
There are tests that have shown that zinc reduces the time patients have a cold by 33 – 35% depending on the dose used. The above studies have shown that zinc helps increase resistance, creating conditions for the body to fight disease.
In general, using zinc to treat colds still needs more careful research. When there are signs of colds or flu, you should use cold medicine appropriately and combine it with micronutrient supplements and zinc to improve effectiveness, helping to quickly recover your health safely.
However, you should consult with a doctor or pharmacist.
11. Helps improve age-related macular degeneration
A study has shown that zinc levels in the eyes of elderly people with age-related macular degeneration (AMD) are lower than those of normal people. Therefore, zinc deficiency can also be a cause of age-related macular degeneration.
In addition to zinc, older people are also recommended to supplement beta carotene, vitamin C and vitamin E to control the condition from getting worse.
12. Improve neurological symptoms
The brain needs a large amount of zinc to enhance function and improve memory, especially in young children. Zinc deficiency can reduce intellectual development in children, cause neurological disorders in adults and some more serious neurological diseases.
A study of neurological symptoms in about 63 patients showed that zinc deficiency led to neurological symptoms including: headaches, paresthesia and peripheral neuropathy.
13. Support sexual health
The effects of zinc on sexual function are also of great interest, especially on male fertility.
Zinc affects sperm quality and fertilization. If there is a zinc deficiency, sperm quality will decrease, mobility will decrease, and the ability to fertilize eggs will decrease. However, supplementing too much of this micronutrient is also toxic to sperm.
In addition, zinc also has a positive effect on testosterone secretion in men, increasing sexual desire and reducing the risk of erectile dysfunction.
14. Improve memory
Zinc plays an important role in the reception of nerve cell information signals, thanks to its ability to regulate ion channels and neuroplasticity.
In a 2017 scientific study, the use of zinc on some rodents showed that zinc can enhance cognition and perform better tasks related to thinking and memory.
In addition, zinc also contributes to the transport of calcium into the brain, so a lack of zinc hinders this transport, making it easy to become irritable.

If there is a lack of zinc, memory ability will also decrease.
15. Foods that provide zinc
It is not difficult to supplement zinc for the body from the daily diet. You can refer to the following zinc-rich foods:
- Shellfish: oysters, clams, shrimp, crab, …
- Nuts: soybeans, red beans, cashews, ….
- Red meat: beef, duck, …
- Fish
- Dairy products
- Whole grains: oats, brown rice.
Note that zinc from animal sources is more easily absorbed than zinc from plant sources. In addition, providing additional zinc from supplements is also an option recommended by doctors.

Zinc is abundant in everyday foods.
16. Signs of zinc deficiency
The cause of zinc deficiency is mostly due to a diet that does not provide enough for the body’s needs. In addition, patients with diabetes, liver disease or cancer also reduce the ability to absorb zinc.
If you have the following symptoms, you may be zinc deficient, go to a medical facility for examination:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Wounds that do not heal
- Lack of alertness
- Reduced sense of smell and taste
- Diarrhea
- Loss of appetite
- Skin ulcers, pimples
17. Notes when using zinc
- Subjects need to be careful when supplementing zinc
- Subjects who are allergic to zinc or foods containing zinc.
- Subjects who are taking antibiotics.
- Subjects who are taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Subjects who are taking blood pressure medication, immunosuppressants, ACE inhibitors.
- Side effects of zinc
While zinc deficiency causes mild symptoms and develops slowly, excess zinc can cause more acute, dangerous symptoms, also known as zinc poisoning:
- Nausea, vomiting, vomiting.
- Abdominal pain.
- Diarrhea.
- Headache.

When you have zinc poisoning, you will feel nauseous and vomit.
Interactions of zinc with drugs
Some drugs that interact with zinc should be taken 2-4 hours apart, because they can reduce the body’s ability to absorb zinc, for example:
- Tetracycline antibiotics, quinolone antibiotics, levoflavoxacin.
- Diuretics.
- Blood pressure medications.
- Minerals: Iron, magnesium, calcium, copper.
So, through the above article, you must have understood the effects of zinc on the body and how to supplement zinc properly. Please share this information with your relatives and friends if you find the article useful!





