Kiwi is a fruit known for its high vitamin C content, which brings many wonderful benefits to human health. So what are the effects of kiwi that make it so popular? Below are the effects of kiwi that make you unable to ignore this fruit.
1 What is Kiwi? Nutritional value of kiwi
Kiwi is a small fruit with a brown skin and green or yellow flesh, rich in vitamin C and antioxidants.
Kiwis are grown in many places, but New Zealand is the leading exporter and most people prefer to eat golden kiwis because the flesh is softer than green kiwis.
Nutritional value of kiwi:
- Protein: 1.14g.
- Carb: 14.7g.
- Fiber: 3g.
- Sugar: 8.99g.
- Calcium: 34mg.
- Iron: 0.31mg.
- Magnesium: 17mg.
- Phosphorus: 34mg.
- Potassium: 312mg.
- Sodium: 3mg.
- Zinc: 0.14mg.
- Copper: 0.13mg.
- Manganese: 0.098mg.
- Vitamin B1: 0.027mg.
- Vitamin B2: 0.025mg.
- Vitamin B3: 0.341mg.
- Vitamin B6: 0.063mg.
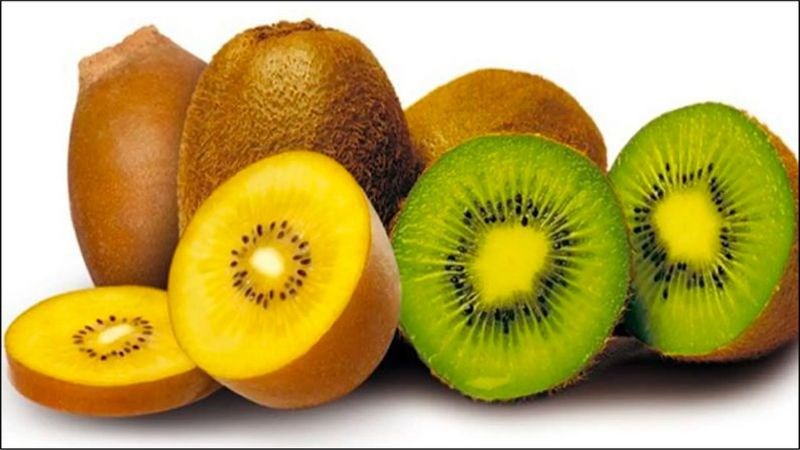

Kiwi is a fruit rich in vitamin C.
2 Benefits of Kiwi
Good for the digestive system
The fiber in kiwi helps promote digestion, helping to treat both constipation and diarrhea. Kiwi also contains potassium, an important electrolyte that also helps the digestive system.
Another important contributing factor here is actinidin, an enzyme found in kiwi. This enzyme also aids digestion, promoting the digestion of protein in food.
The fiber in kiwi promotes digestion.
Aids in Weight Loss
Kiwis are a low-calorie fruit (55.5 calories for 91g of kiwi) and contain negligible fat, while also being rich in fiber. All of this just makes them an ideal food for a weight loss diet.
You can replace other high-calorie foods in your diet with kiwis. When combined with exercise and a healthy lifestyle, kiwis can aid in weight loss effectively and safely.

Kiwi is an ideal fruit in weight loss regimes.
Helps control diabetes
Kiwis are high in fiber, especially soluble fiber. Fiber helps slow down the digestion and absorption of sugar in the blood, helping to control the increase in blood sugar after eating.
At the same time, kiwis have a much lower glycemic index than many other fruits. This means that when you eat kiwis, you don’t have to worry about a sudden increase in blood sugar.
In addition, kiwis are high in vitamin C and antioxidants that help fight inflammation and protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. Kiwis help improve the body’s response to insulin.
However, you should note that kiwis are only part of an overall diet that helps control diabetes. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, eating a variety of fresh foods and exercising regularly are important for effective diabetes control.

Kiwis have a much lower glycemic index than many other fruits.
Boosts Immunity
Kiwis are rich in Vitamin C, which helps regulate the body’s immune response. In fact, kiwifruit contains about 230% of the recommended daily intake of Vitamin C, and the fruit provides a host of immune-boosting nutrients in every serving.
Kiwis are also rich in antioxidants. Antioxidants help eliminate free radicals in the body and reduce oxidative stress. This property can protect the body from inflammation and disease.
Vitamin C helps regulate the body’s immune responses.
Rich in antioxidants
One of the reasons kiwi is called a superfood is because it contains a large amount of antioxidants such as vitamin C, vitamin E that can fight the destruction of free radicals. (See more vitamin E products that help the body fight infections, reduce the risk of plaque formation in the arteries and heart disease.)
A recent study in 2020 showed that vitamin C in kiwi can reduce cancer growth by reducing oxidative damage and increasing intestinal motility. This can help prevent cancers such as colorectal cancer.
In addition, the vitamin E component in kiwi helps reduce cholesterol effectively and fight free radicals. Kiwi is also rich in polyphenols with immune-stimulating activity. These polyphenols have been shown to promote the response of the immune system.

Kiwis are also rich in antioxidants.
Anti-inflammatory
Kiwellin and Kissper are proteins in kiwifruit that may have anti-inflammatory properties. Studies have shown that Kissper has an effective anti-inflammatory effect in the intestine.
At the same time, the anti-inflammatory effect of kiwifruit is also achieved thanks to antioxidants such as vitamins, quercetin or lutein, which help prevent the effects of free radicals and prevent inflammatory reactions from occurring.
The anti-inflammatory properties of kiwi are due to Kiwellin and Kissper.
Good for the cardiovascular system
Kiwis are rich in fiber, potassium and antioxidants, which play an important role in maintaining cardiovascular health.
The potassium contained in kiwis helps dilate blood vessels, helps manage blood pressure, and reduces the tendency to develop cardiovascular diseases. In addition, thanks to the fiber content, consuming kiwis will help reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases and reduce bad cholesterol.
Potassium contained in kiwi helps protect the heart
Prevents Blood Clots
Some studies have also shown that kiwi fruit extract contains anticoagulant compounds . This can help you prevent the risk of stroke, heart attack and some other cardiovascular diseases.

Kiwi has the ability to reduce the aggregation of blood clots.
Reduces symptoms of asthma, respiratory diseases
Like other fruits rich in vitamin C, kiwi is also considered to be highly effective in treating respiratory diseases. Tests were conducted on a number of subjects with asthma as well as respiratory diseases.
As a result, studies have shown that providing vitamin C from fruits such as kiwi can alleviate symptoms such as wheezing, stuffy nose and sore throat. (See more products of vitamin C to boost immunity, supplement essential nutrients).

Vitamin C reduces asthma symptoms
Improves eyesight
Kiwis are a rich source of lutein, which not only protects the skin from UV rays and degeneration, but also prevents eye diseases such as macular degeneration.
In addition to lutein, kiwis also provide large amounts of carotenoids and vitamin A, compounds that have been shown to be beneficial for optimal eye health.

The vitamin A content in kiwi is necessary to improve eyesight.
Liver protection
Kiwis contain a special compound called pyrroloquinoline quinone, which is effective in treating fatty liver caused by alcohol. In addition, the antioxidant compounds in kiwis can also prevent the effects of free radicals, contributing to protecting liver cells from the risk of inflammation.
Kiwi has been shown to be effective in treating alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Preventing kidney stones
Kiwis’ kidney stone prevention effect is due to the potassium content in them. According to nutrition experts, potassium in kiwis has the ability to prevent the formation of kidney stones, thereby helping you avoid kidney stones.
The potassium content in kiwi helps prevent the formation of kidney stones.
Preventing iron deficiency anemia
Kiwi itself is not a major source of iron, however, it is one of the best natural sources of vitamin C. The presence of vitamin C significantly increases the ability to absorb iron, effectively preventing iron deficiency.
In a study comparing the group that consumed two kiwis for breakfast compared to one banana, the results showed that the group that ate kiwi had a higher increase in serum ferritin concentration than the group that ate banana.
Vitamin C significantly increased iron absorption.
Beauty support, anti-aging
Collagen is an important protein in our body and helps maintain skin, muscles, bones and tendons. Research shows that it breaks down as we age and will depend on the concentration of vitamin C, which we know is abundant in kiwifruit.
At the same time, the polysaccharides in kiwi can double the ability to synthesize collagen. Moreover, kiwi is also a rich source of lutein, an antioxidant that can protect the skin from UV rays.

Aging can be improved by kiwi
Helps Sleep Better
Serotonin may be the reason why this fruit is famous for its sleep-aiding properties. The serotonin in kiwi has been shown to increase sleep duration and sleep efficiency by 13% and 5%, respectively.
In addition, the serotonin in kiwi also helps enhance memory, improve mood and support the treatment of depression.

The hormone serotonin will help you get a deep sleep.
Good for hair
Kiwi contains a large amount of vitamin E, which promotes hair growth, helps hair grow quickly and strong. Besides the high amount of vitamin E, kiwi is also rich in antioxidants that help enhance hair growth and quality.

Nutrients in kiwi can improve hair quality
Cancer Prevention
Kiwi fruit extract shows promising potential against nasopharyngeal cancer cell lines, reducing DNA oxidation. Vitamin C in kiwifruit fights free radicals, significantly reducing the risk of cancer.
The fiber in kiwi is also an effective anti-cancer agent, especially intestinal cancer. Studies on mice have shown that thanks to the polysaccharides and abundant antioxidants in fresh kiwi nutrition, they have the ability to fight tumors and prevent cancer cells.

Antioxidants can help prevent cancer effectively
Good for pregnancy
Kiwis contain folate, which is essential for cell division. During pregnancy, doctors always advise women to supplement folate because it can protect the fetus from birth defects, such as neural tube defects.

Kiwi is a natural source of folate for pregnant women
Strengthening bone and joint health
Kiwi contains many beneficial components for the bone system such as potassium, calcium and phosphorus, contributing to building a healthy bone system. Supplementing potassium with kiwi can also help prevent osteoporosis.

Kiwis may help prevent osteoporosis
Prevents bacterial and fungal infections
Both green and gold kiwifruit have shown antibacterial and antifungal properties. This effect is particularly strong in kiwifruit seeds. Kiwifruit extracts have shown antibacterial activity against several strains of bacteria.
Golden kiwifruit contain a protein called actinchinin, which is thought to be the source of their antifungal properties.
Antifungal and antibacterial properties are present in both green and gold kiwis.
Speeds up wound healing
The most common micronutrients in kiwi are vitamin C and vitamin K, both of which play an important role in wound healing.
Vitamin C is a precursor to collagen, a structural component of your skin. It is also a powerful antioxidant that supports your body’s natural repair mechanisms.
To prevent excessive bleeding, vitamin K promotes timely blood clotting. It also increases bone strength and prevents fractures.
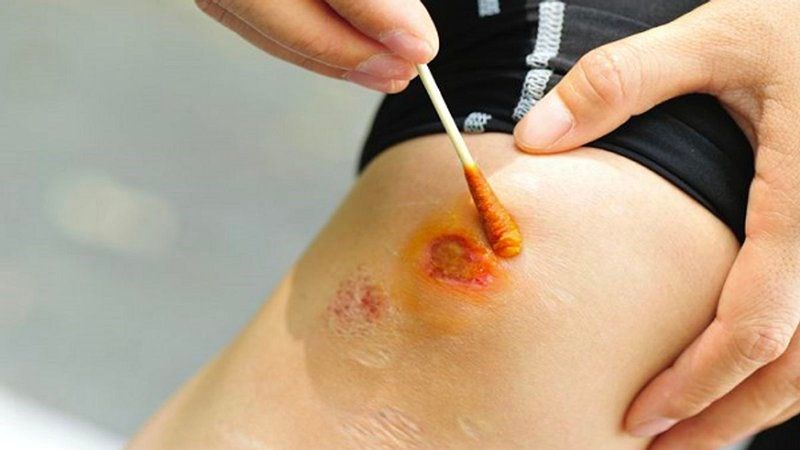
Add kiwi when there is an open wound.
3 Notes when eating kiwi
People who should not eat kiwi
Although kiwi has many beneficial effects on the body, in some cases kiwi can be contraindicated because it can cause adverse effects:
- People with latex allergies: It has been found that most people with latex allergies are also susceptible to kiwi allergies. If you have an allergic reaction to latex, you should avoid eating kiwi and products containing kiwi.
- People who are taking certain medications: Kiwi can increase the feeling of addiction when used with antifungal drugs and lower blood pressure too much when used with drugs to treat high blood pressure.
- Patients with pancreatitis: Eating too much kiwi can lead to acute pancreatitis.
- People with weak digestive systems: Kiwi can cause digestive problems such as vomiting, nausea, diarrhea, bloating, chills, sweating, difficulty swallowing.
- Patients with kidney stones and gallstones: The high oxalate content in kiwi can form kidney and gallstones, so these people should avoid using it.
- People with frequent urination: Kiwi has a diuretic effect, causing patients to urinate frequently.
- Gout patients: Using kiwi can increase uric acid levels in the body, which can trigger acute gout attacks.
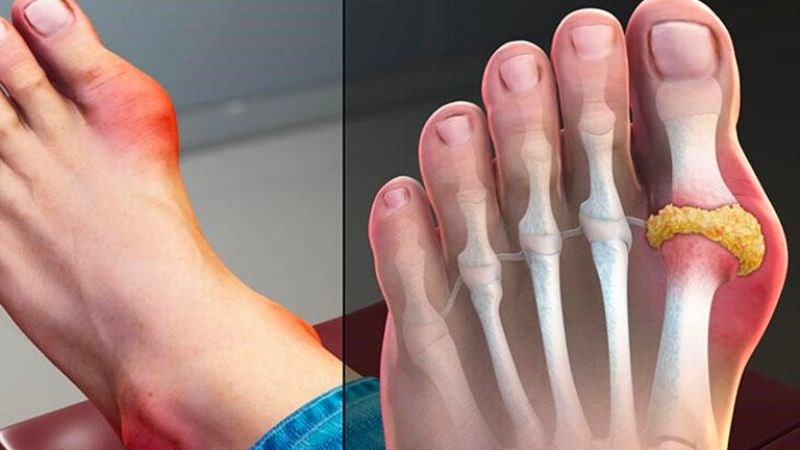
Uric acid accumulation may be worse if gout patients consume kiwi.
Notes on selecting and storing kiwis
When selecting and storing kiwis, there are some important notes to ensure that you will have fresh and safe kiwis to consume. Here are some important notes:
When selecting kiwis:
- Color and appearance: Choose kiwis that are dark green, not peeling or cracked. Kiwis should be evenly colored and have no swelling or signs of damage.
- Softness: Kiwis should be slightly soft when lightly pressed with your finger. If they are too soft or too pliable, the kiwis may be overripe and rotten.
- Smell: Kiwis should have a mild, sweet smell. If they have an antibacterial or other unusual smell, it may be a sign of spoilage.
When storing kiwis:
- Storage temperature: Kiwis should be stored at room temperature or in the refrigerator. The ideal temperature for storing kiwis is between 0 degrees Celsius and 4 degrees Celsius (32 degrees Fahrenheit and 39 degrees Fahrenheit).
- No Ethylene Gas: Avoid exposing kiwis to ethylene gas, which can cause kiwis to ripen too quickly or spoil. Store kiwis separately from other fruits and vegetables.
- Store Separately: Kiwis can emit an enzyme called actinidin, which can cause other fruits and vegetables next to them to ripen too quickly. Therefore, store kiwis separately or in fruit bags to prevent them from coming into direct contact with other foods.
- Do not wash before storing: Do not wash kiwis before storing, as water can cause kiwis to spoil quickly. Wash kiwis before eating or using.
- Storage Time: Fresh kiwis can be stored in the refrigerator for 1 to 4 weeks, depending on their initial ripeness and storage conditions.

Proper storage can help kiwis retain their nutrients well.
Notes when eating kiwi
Some foods that are incompatible with kiwi include:
- Cucumber: Some enzymes contained in cucumbers will decompose vitamin C in kiwi, thereby reducing the amount of this vitamin in kiwi.
- Carrots: The nutritional value of both foods will be significantly reduced because the ingredients have the ability to decompose each other.
- Crab: The compound arsenic pentavalent combined with vitamin C in kiwi can cause poisoning in humans.
- Cow’s milk: Do not combine milk as well as dairy products with kiwi because the reaction of protein in milk with vitamin C will cause symptoms of discomfort, stomach pain and diarrhea.
- You should eat the kiwi skin, because the kiwi skin is quite safe and contains many vitamins, nutrients and antioxidants.
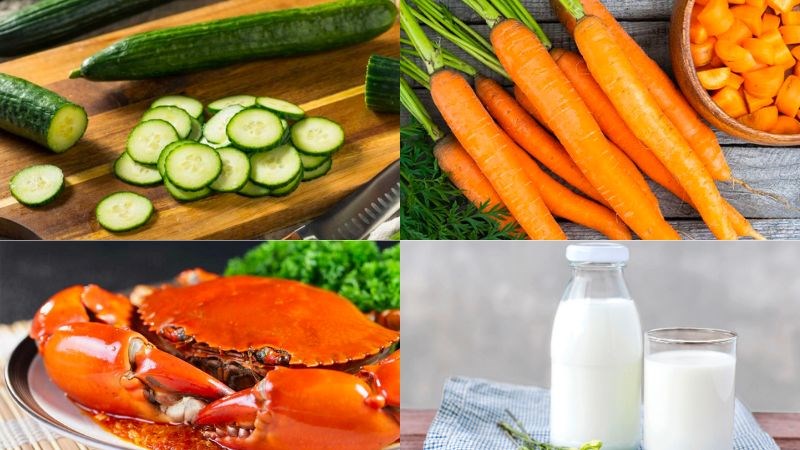

Foods to avoid when using with kiwi
Hopefully this article will provide you with a lot of useful knowledge about the effects of kiwi. Although kiwi contains many beneficial nutrients, it should be supplemented with other nutrients at the same time, and should not be overused. If you find this article useful, please share it with your relatives and friends!





