Vitamin A (also known as retinol) is an essential substance for humans belonging to the group of fat-soluble vitamins. In some foods of animal origin, the main form of vitamin A is retinol, but it can also exist in the form of retinal or retinoic acid.
Continuous deficiency of vitamin A will produce a series of changes, the most destructive of which occurs in the eyes. Visual changes are collectively known as xerophthalmia.
First is the drying of the conjunctiva due to the epithelium of the tear and mucus glands being replaced by keratinized epithelium. This is followed by the accumulation of keratin debris into small translucent patches, and finally the erosion of the rough horny membrane surface with degeneration, destruction of the cornea and total blindness.
Therefore, vitamin A is indicated for the treatment of diseases such as dry eyes, night blindness, slow growth in children, susceptibility to respiratory infections, acne, dry and brittle skin, hair and nails, and for rapid healing of wounds and burns.
Because vitamin A is fat-soluble, it is more difficult to excrete excess dietary intake than water-soluble vitamins. Therefore, overdose can lead to vitamin A toxicity.
It can cause nausea, jaundice, allergic reactions, anorexia, vomiting, blurred vision, headache, muscle damage, lethargy, and mood changes. Acute toxicity generally occurs at doses of 25,000 IU/kg and chronic toxicity occurs at 4,000 IU/kg per day for 6-15 months.
However, liver toxicity can occur at levels as low as 15,000 IU/day, with the average toxic dose being 120,000 IU/day.
In people with impaired kidney function, 4,000 IU/kg per day can cause significant damage. Heavy alcohol use can also increase vitamin A toxicity.
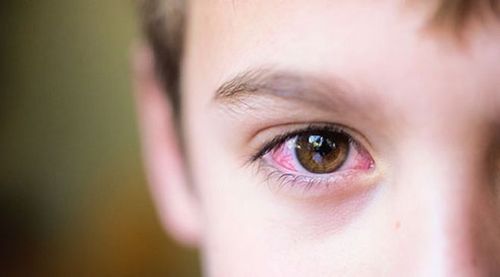
Dry eyes due to vitamin A deficiency
In chronic cases, hair loss, dry mucous membranes, fever, fatigue, weight loss, bone fractures, anemia, and diarrhea may be the leading symptoms associated with less severe poisoning.
The above symptoms of poisoning only occur when taking vitamin A supplements orally. Carotenoids (such as beta carotene in carrots) do not cause such symptoms. Therefore, vitamin A supplementation through food is safer.
A recent study that showed a correlation between low bone mineral density and high vitamin A intake also warned that overdose of this vitamin can cause bone diseases.
Note that vitamin A dosage is usually expressed in international units (IU) or retinol equivalents (RE), with 1 IU = 0.3 micrograms of retinol. The absorption of provitamin A also depends largely on the amount of lipids ingested at the same time as the food. Therefore, users of this drug need to strictly follow the recommended dosage and pay attention to a fatty diet while taking the drug.





