Benign thyroid tumors are tumors that develop within the thyroid parenchyma. The disease is usually not life-threatening but can cause thyroid dysfunction, thereby affecting physical and mental health. Currently, there are many effective treatment methods depending on the symptoms, nature and size of the tumor.
Factors for the development of benign thyroid tumors
Benign thyroid tumors are a type of tumor that develops in the thyroid gland without the ability to invade surrounding structures. Although benign tumors are not life-threatening, they still require treatment as prescribed by a doctor.
The root cause of benign thyroid tumors has not been determined exactly, but there are a number of factors that can play a role in the formation and development of tumors. Below are some of the main factors considered to be the cause of thyroid tumors, specifically:
- Genetic factors: Genetics is considered an important factor in causing thyroid tumors. If a family member has a thyroid tumor, the risk of developing a thyroid tumor in relatives will be higher.
- Thyroid hormone imbalance: An increase or decrease in thyroid hormone levels in the body can contribute to the formation of a thyroid tumor. Some causes of thyroid hormone imbalance include thyroiditis, a diet with too much or too little iodine, multinodular goiter, etc.
- Environmental impact: Pollution, dust, frequent exposure to toxic substances and chemical additives can affect the thyroid gland, contributing to the formation of tumors.
- Thyroid disease: Thyroid-related problems such as thyroiditis, goiter or structural abnormalities of the thyroid gland can cause the development of benign thyroid tumors.

Frequent exposure to chemicals may be a factor in tumor development.
Signs of benign thyroid tumors
Clinical manifestations of benign thyroid tumors
Symptoms of benign thyroid tumors can vary depending on the size, location and nature of the tumor. Common manifestations in patients include:
- Increased size of the thyroid gland: Tumors from small to large can compress the neck area, creating a feeling of swelling, choking, difficulty speaking, dry cough or difficulty swallowing. The tumor can be seen or felt when touched.
- Voice changes: This is one of the typical signs of benign thyroid tumors. Thyroid tumors can put pressure on the vocal cords, causing changes in the voice. The voice can become hoarse, deep and difficult to hear.
- Fatigue, weakness: Benign thyroid tumors can affect thyroid function, causing symptoms of fatigue, weakness.
- Weight changes: Thyroid dysfunction can cause unexplained weight changes. Some people may gain weight despite eating less, while others may lose weight despite eating more. Symptoms often appear with digestive disorders, difficulty sleeping or menstrual cycle disorders.
Although benign thyroid tumors are not life-threatening, regular monitoring and examination by a specialist is still required.

What are the symptoms of benign thyroid tumors?
Paraclinical results
When a benign thyroid tumor is suspected, paraclinical methods are used to determine the size, location, and nature of the tumor. Some commonly prescribed tests include:
- Thyroid ultrasound: Thyroid ultrasound is a common paraclinical method used to examine the size, shape, and structure of the thyroid tumor. Ultrasound results can show the location and nature of the tumor, helping to determine whether the tumor is benign or malignant.
- Blood tests: Blood tests can provide information about the level of thyroid activity, and assess the increase or decrease in thyroid hormones such as TSH, T3, and T4. Blood test results can reflect abnormal manifestations related to benign thyroid tumors.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT scan): Both MRI and CT scan of the thyroid can provide detailed images of the thyroid tumor, helping to determine the size, location, and nature. The results from these methods can help distinguish benign from malignant tumors.
- Fine needle aspiration (FNA): Thyroid aspiration is a diagnostic procedure in which a sample of cells is taken from a thyroid nodule using a small needle. The cells are examined under a microscope to determine whether they are benign or malignant. The results from the FNA technique can provide the most accurate information about the nature of the tumor.
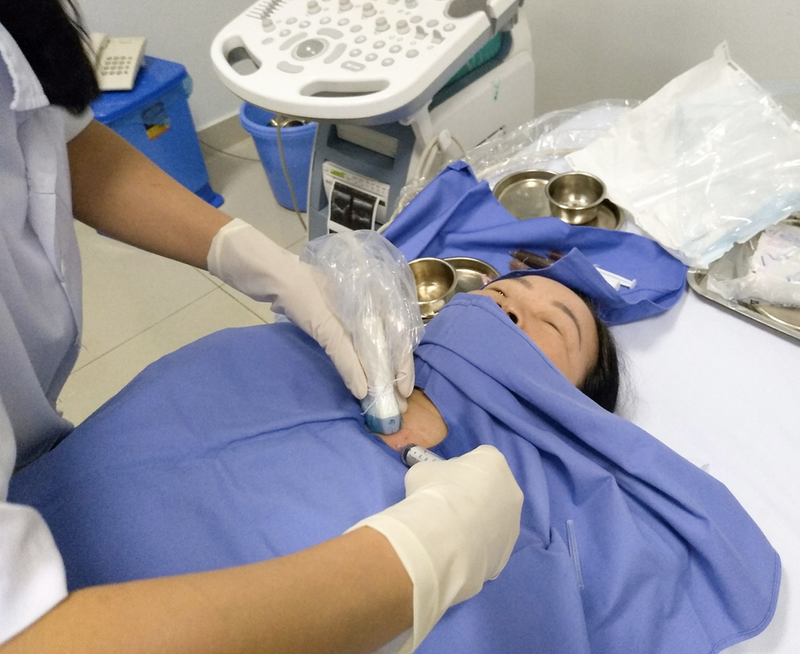
Benign thyroid tumor ultrasound helps assess the nature, size and location
Treatment of benign thyroid tumors
So are benign thyroid tumors dangerous? This is a common medical condition, usually not life-threatening. However, in some cases, when the tumor causes uncomfortable symptoms for the patient or is at risk of malignant transformation, specialized treatment intervention will be required.
Here are some methods of treating benign thyroid tumors that are applied depending on each patient’s case, specifically:
- Monitoring and observation: For benign tumors that are small in size, do not cause symptoms or do not significantly affect health, the doctor may recommend close monitoring and observation. This requires compliance with periodic examinations with thyroid ultrasound to monitor the size and nature of the tumor.
- Thyroid hormone therapy: This is a treatment for benign thyroid tumors that are about 2 to 3 cm in size. The commonly used drug is levothyroxine, which enhances thyroid function, thereby limiting the proliferation of
- thyroid follicular cells. Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be considered to remove benign thyroid tumors. This is usually performed for tumors larger than 4cm or when the patient exhibits severe symptoms such as esophageal compression, difficulty breathing, difficulty swallowing, etc. Surgery involves removing part or all of the thyroid gland.
Through the above article, Long Chau Pharmacy would like to send readers information about benign thyroid tumors including risk factors, symptoms as well as treatment for this condition. Please continue to read articles with many rich topics!





