Currently, the incidence of thyroid diseases is increasing, especially goiter. This is a type of thyroid metabolic disorder, which is almost harmless and can be completely cured if detected early. Let’s learn about goiter and what you need to know through the following article!
What is goiter?
The thyroid gland is part of the body’s endocrine system, shaped like a butterfly located under the cartilage and on the front of the neck. The thyroid gland consists of two lobes, left and right, connected to each other through the isthmus. With the important task of producing hormones, the thyroid gland helps control the body’s metabolism and some other functions such as digestion, circulation, cardiovascular system, etc.
Goiter, also known as thyroid nodules, is a condition in which thyroid cells develop abnormally, forming one or more nodules in the thyroid. Depending on the condition of each person, thyroid nodules can be single or multiple, benign or malignant. Most thyroid nodules do not cause symptoms and are often discovered incidentally when performing a neck ultrasound for another reason.
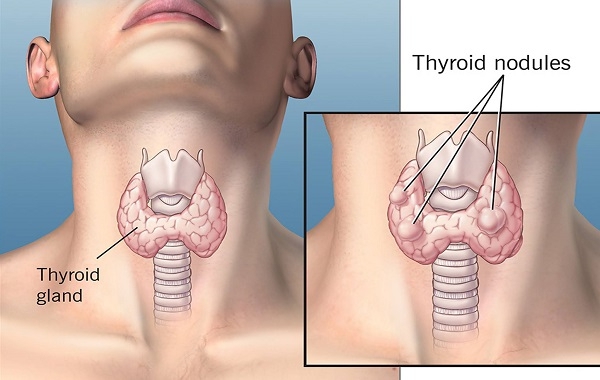
Goiter is a condition in which thyroid cells grow abnormally.
Goiter is divided into many different types:
- Colloid nodule: This is a condition in which thyroid tissue grows excessively, however, this growth is benign, although it can still grow larger, it will not invade other cells.
- Thyroid cyst: The formation of cystic tissue, which may contain fluid or fluid mixed with solid thyroid tissue.
Inflammatory nodules: Chronic inflammation that lasts for a long time, the patient may experience pain or no pain. - Multinodular goiter: Thyroid cells grow to form many nodules and most of these cases are benign.
Hyperthyroidism: The thyroid gland develops abnormally, causing more hormones to be produced than normal. This condition causes many effects on the body such as rapid heartbeat or sudden cardiac arrest, high blood pressure, osteoporosis, etc. - Thyroid cancer: The incidence of thyroid cancer accounts for about 5% of all cases of goiter.
Causes of goiter
Goiter is a complex disease, originating from many different causes. Specifically:
Thyroid tissue develops excessively, uncontrolled compared to normal, creating tumors inside the thyroid gland. However, the exact cause of thyroid tissue development has not yet been found. The danger level of thyroid tissue development is not too serious for the patient. However, if the size of the thyroid nodule is too large, it can cause compression on the thyroid gland, causing other effects.
Thyroid cyst: Is a condition where there is a certain amount of fluid inside the thyroid gland. People with thyroid tumor degeneration will often have this condition. According to research, most cysts will not be the cause of cancer, but the solid tissue inside can still increase the risk of cancer.
There are many causes of goiter.
Chronic thyroiditis: Known as Hashimoto’s, a disorder that causes the thyroid gland to become inflamed and develop large nodules, the patient often appears with symptoms of hypothyroidism.
Multinodular goiter: The thyroid gland grows to a large size, the cause may be due to a disorder or lack of iodine. Usually, the thyroid nodules exist separately inside.
Iodine deficiency: Studies have shown that if you do not or use little iodized salt in your daily diet, it can increase the risk of forming nodules inside the thyroid gland.
Signs of thyroid goiter
Goiter diseases are often not easy to detect, only detected when the thyroid nodules have grown to a large size, causing discomfort. Late detection causes many difficulties in the treatment process, and also prolongs the treatment time. When the newly formed thyroid nodules are very small, it is very difficult to detect. As these nodules grow, they cause some recognizable symptoms. Here are some common symptoms in people with goiter:
- Feeling sick as if there is something inside the thyroid gland.
- Feeling difficult to swallow when eating and sometimes feeling short of breath due to the growing thyroid nodule causing compression on the esophagus and trachea.
- In some cases, goiter can be observed inside the neck, the most common location of the goiter is the front of the neck.
- The body is tired, has frequent bowel movements, poor heat tolerance, and increased sweating.

As the thyroid grows larger, it causes specific symptoms that can be observed with the naked eye.
In some cases, when the thyroid gland develops, the thyroxine hormone level increases too high, causing some symptoms such as:
- Sudden weight loss for unknown reasons;
- The body often sweats a lot;
- Hands shake;
- Frequently feel anxious, nervous;
- Unstable heart rate, irregular heartbeat, rapid heartbeat, irregular increase or decrease in heart rate;
- In women, it can cause irregular menstruation…
Complications of goiter
Many people worry, can goiter develop into cancer? In fact, not all goiters cause cancer, but it can still lead to other serious complications, such as:
- The development of goiters causes compression of internal organs in the neck such as the trachea and esophagus, causing difficulty swallowing or difficulty breathing.
- Hyperthyroidism: Occurs when the thyroid gland proliferates and produces a large amount of thyroid hormone. Some symptoms of hyperthyroidism include anxiety, agitation, muscle weakness, weight loss, rapid heart rate, etc.
- Potential for arrhythmia or acute thyrotoxicosis. Of which, acute thyrotoxicosis is considered an extremely dangerous complication, threatening the patient’s life.
- In cases where a goiter has been surgically removed, one side of the thyroid nodule must be removed, the patient may have to use thyroid hormone replacement to avoid hormone deficiency.
Hyperthyroidism is one of the common complications of goiter.
Methods for diagnosing goiter
Doctors often use the following methods to diagnose goiter:
Thyroid ultrasound
This is an imaging test method based on the frequency of sound waves to create a real image of the thyroid gland inside. After performing a thyroid ultrasound, the doctor will receive clear characteristics, including the structure and shape (of the thyroid nodule), assess whether this nodule is benign or malignant, from which the doctor will take further measures to explore the thyroid nodule.
Thyroid nodule biopsy by fine needle
The method of thyroid nodule biopsy by fine needle plays an important role and is widely recognized and used in Vietnam and around the world. The doctor will use a small needle to puncture the thyroid gland to aspirate fluid or cells, then examine them under a microscope. The test results can infer the nature of the nodule as benign or malignant. In some cases where the results are unclear or suspicious, a second biopsy will be required.
Thyroid scintigraphy
The purpose of this method is to assess the condition of the thyroid nodules inside. With this test, the patient’s body can receive a small amount of radioactive iodine, then the doctor will check whether the thyroid tissue is functioning normally by observing whether the amount of radioactive iodine is absorbed into the thyroid tissue or not.
Hopefully, through the above article, readers have better understood the severity of goiter. Learning about goiter and what you need to know will contribute to raising awareness of protecting the health of yourself as well as those around you, early detection of thyroid disease also contributes to improving the effectiveness of treatment.





