Thyroid tirads 3 is not a new term, but not everyone has full awareness of this disease. How dangerous is it and how to accurately determine that it is thyroid tirads 3? Let’s answer that question right in this article!
What is thyroid tirads 3?
The thyroid is an endocrine gland that plays an extremely important role in the human body. This is where the main hormones that directly participate in the body’s regulation and metabolism are produced.
The thyroid gland is divided into two lobes, the left lobe and the right lobe, which are connected by the thyroid isthmus. When one of these two lobes has a thyroid nodule, the patient will be clinically examined by a doctor and assigned tests to classify the thyroid nodule.
Among the types of thyroid nodules, thyroid tirads 3 is a mostly benign nodule and the risk of malignancy is only a small part, about 1.7%. However, patients should not be too subjective, because if the malignancy rate is not detected and treated promptly, it can lead to dangerous complications. To determine accurately, the patient will need to have a biopsy, which is a method of aspirating cells for testing.
Thyroid tirads 3 are mostly benign lesions.
Is thyroid tirads 3 dangerous?
Unlike most other thyroid diseases, thyroid nodules often do not show symptoms and can only be detected through regular health check-ups of the patient.
To determine whether thyroid tirads 3 is dangerous or not and at what level, the patient needs to perform tests to classify the malignant or benign potential of the thyroid nodule, including:
- Thyroid tirads 1: These are benign lesions.
- Thyroid tirads 2: The lesions are benign and have no risk of malignancy.
- Thyroid tirads 3: Most lesions are benign, only about 1.7% are malignant.
- Thyroid tirads 4: Lesions have signs of suspected thyroid malignancy. In which it is divided into other groups including: Malignant 3.3%, malignant 9.2%, malignant 44.4 – 72.4% and malignant.
- Thyroid tirads 5: This is the most severe form of damage with a malignant rate of up to 87.5%.
According to the above classification tests, most patients with thyroid tirads 3 are mostly benign. However, although only a few are malignant, there are still cases of dangerous complications leading to cancer.
In addition, when having thyroid tirads 3, the tumor will gradually grow larger and compress the esophagus, trachea, causing difficulty in swallowing and breathing. More dangerously, some cases of patients are also likely to have acute cough attacks. In addition, the nerves around the neck and larynx will also be affected if the goiter grows larger. At this time, the patient will experience symptoms such as hoarseness and loss of voice. At the same time, the patient’s heart may beat faster and blood pressure may increase due to the thyroid nodule and cause hyperthyroidism symptoms.
Thyroid tumor tirads 3 causes difficulty breathing in patients due to compression
How to accurately determine if it is a tirads 3 thyroid gland?
Because the tirads 3 thyroid gland often does not have specific, clear symptoms, it is difficult for patients to know for themselves whether they are sick or not. Therefore, patients should go to the nearest reputable hospital or medical facility to be examined and evaluated by a doctor. In order to know exactly what health condition they are experiencing, and at the same time determine whether they have a tirads 3 thyroid gland.
Currently, commonly prescribed testing methods include:
- Thyroid ultrasound: With this technique, doctors will be able to detect the location, quantity and nature of thyroid nodules. At the same time, ultrasound also helps evaluate the lymph nodes in the patient’s neck. Based on the information obtained during the thyroid ultrasound, you will be diagnosed with whether it is a tirads 3 thyroid gland or not.
- Thyroid function test: Including TSH, T3, total T4 and other indicators such as TG, Anti TG, Calcitonin.
According to the classification of ACR TIRADS 2017:
- If the thyroid nodule is > 2.5cm in size, a biopsy will be indicated.
- If the thyroid nodule is > 1.5cm and < 2.5cm in size, a periodic follow-up of about 6 months will be indicated. However, due to the need and depending on the actual situation of the patient, most nodules larger than 1cm will be indicated for a biopsy.
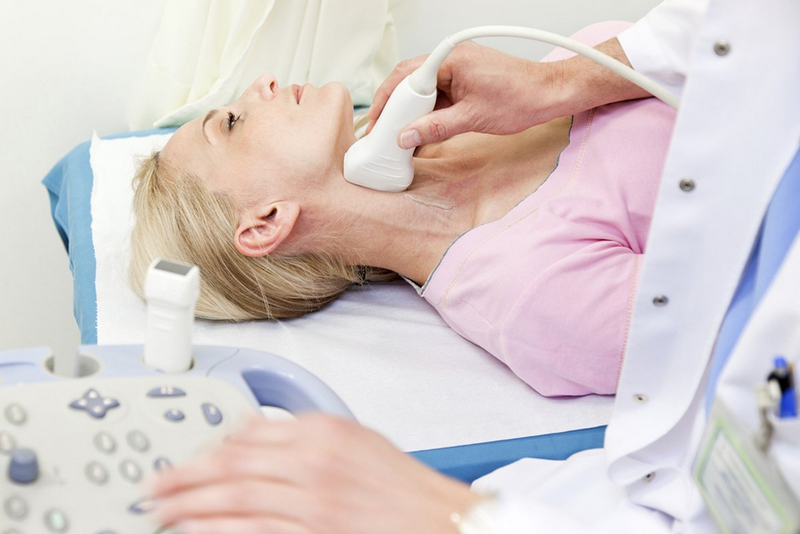
Thyroid ultrasound is a highly accurate testing method.
Thyroid treatment tirads 3
After examination and diagnosis, if the thyroid nodule is benign and small in size, the patient will not need to worry too much. Instead, just follow the doctor’s instructions, maintain regular exercise, always keep a comfortable spirit and a scientific lifestyle. In addition, the patient should pay attention to the hospital or medical facility for periodic check-ups about 3 – 6 months / 1 time.
In case the thyroid nodule is large and causes symptoms of compression, the patient will undergo surgery or use high-frequency radio wave ablation to treat the tumor.
Particularly for malignant thyroid tirads 3 or thyroid cancer, the tumor must be removed by surgical intervention, then treated with chemotherapy.
Patients need surgery if thyroid cancer is detected.
What should patients prepare before tirads 3 thyroid surgery?
When thyroid surgery is indicated in benign cases with large or malignant thyroid nodules, the notes that patients need to pay attention to include:
- Always keep a relaxed spirit.
- Do not stay up late before surgery and do not use addictive stimulants.
- Do not eat greasy and indigestible foods.
- Only eat light meals and the last meal before surgery must be 8 hours after the surgery.
- The patient will have their blood pressure, breathing rate, body temperature measured… when all conditions are guaranteed, surgery will be performed.
The above article has provided readers with specific issues surrounding tirads 3 thyroid. Hopefully, with this information, you have equipped yourself with the necessary health knowledge. Don’t forget to follow and accompany us in other useful sharing articles!





