Toxic thyroid adenoma can cause many dangerous health complications if not detected and treated promptly. So what are the symptoms of toxic thyroid adenoma? What are the diagnosis and treatment methods?
What is toxic thyroid adenoma?
Toxic thyroid adenoma is a type of thyroid goiter that produces too much thyroid hormone. Toxic thyroid adenoma is also known as toxic nodular goiter. The thyroid is a small gland located in the neck that produces thyroid hormone. Thyroid hormone controls many functions of the body, including heart rate, body temperature, and metabolism.
Toxic thyroid adenoma can originate from a simple goiter and is common in older people, especially women over 55. Children rarely get this disease. Most people with toxic thyroid adenoma have had a goiter with nodules or nodules for many years. Sometimes the thyroid gland is only slightly enlarged and the goiter is not diagnosed.
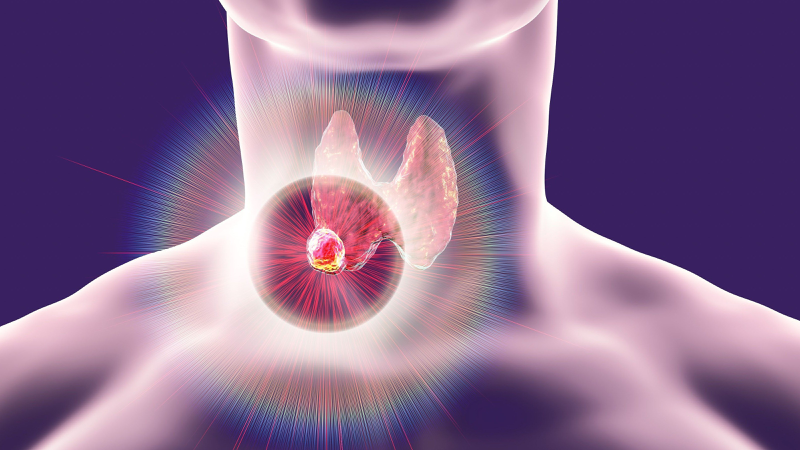
Toxic thyroid tumor is a disease that occurs in the thyroid gland.
Symptoms of Toxic Thyroid Adenoma
Symptoms of a thyroid adenoma may be similar to those of hyperthyroidism:
- Weight loss;
- Increased appetite;
- Anxiety, restlessness;
- Increased sweating;
- Fatigue;
- Muscle cramps;
- Frequent bowel movements;
- Irregular menstrual periods (in women).
In older people, patients may experience signs such as tremors, rapid heartbeat, rapid pulse, atrial fibrillation, heart failure, fatigue, weight loss, depression, and dementia.
Risk of Toxic Thyroid Adenoma
The risk of Toxic Thyroid Adenoma is higher in the following groups:
- Women are at higher risk of Toxic Thyroid Adenoma than men, especially middle-aged women.
- Family history of thyroid disease. If you have a family member with thyroid disease, you are at higher risk.
- People with iodine deficiency. Iodine is a mineral that is necessary for the production of thyroid hormones. Iodine deficiency can lead to hypothyroidism, a condition in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones.
- The risk of developing toxic thyroid nodules increases with age.
- Exposure to radiation from medical treatments can increase the risk of developing thyroid nodules.
- Having a history of thyroid disorders.
In addition, a number of other factors can also increase the risk of toxic thyroid nodules, including: Smoking, obesity, metabolic syndrome, alcohol,…
Middle-aged women are at high risk of developing toxic thyroid tumors.
Diagnosis of toxic thyroid nodules
Most patients with toxic thyroid nodules do not have specific symptoms. Therefore, regularly screen and see a doctor when there are unusual signs to be diagnosed and have a treatment method.
Regular neck check
A regular neck check is an effective way to detect thyroid nodules, including toxic thyroid nodules. When your doctor examines your neck, they will check the size, shape, and location of the thyroid gland. If your doctor finds an abnormal nodule, they may ask you to do additional tests to make a diagnosis.
Imaging tests
Imaging tests can help your doctor determine the size, shape, and location of a thyroid nodule. Imaging tests commonly used to diagnose toxic thyroid nodules include:
- Thyroid ultrasound: Ultrasound is a noninvasive test that uses sound waves to create images of the thyroid gland.
- Thyroid computed tomography (CT) scan: A CT scan is a test that uses X-rays to create images of the thyroid gland.
- Thyroid magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): An MRI is a test that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create images of the thyroid gland.
Blood tests
Blood tests can help your doctor evaluate the function of your thyroid gland. Blood tests commonly used to diagnose toxic adenomas include:
- TSH: TSH is thyroid-stimulating hormone produced by the pituitary gland. TSH helps regulate thyroid hormone production.
- T4: T4 is a thyroid hormone produced by the thyroid gland.
- T3: T3 is a thyroid hormone produced by the thyroid gland and the liver.
Fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC)
Fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) is a simple, safe procedure that is performed in the office. It uses a small needle to remove cells from a thyroid nodule to send to a laboratory for analysis. The results of an FNAC can often help determine whether a thyroid nodule is cancerous. However, in some cases, the test results may be unclear and additional tests may be needed.
Thyroid Biopsy
A thyroid biopsy is a more invasive procedure than an FNAC, in which a sample of thyroid tissue is removed and sent to a laboratory for analysis. A thyroid biopsy is usually performed if the results of an FNAC are inconclusive or if your doctor suspects that a thyroid nodule is cancerous.
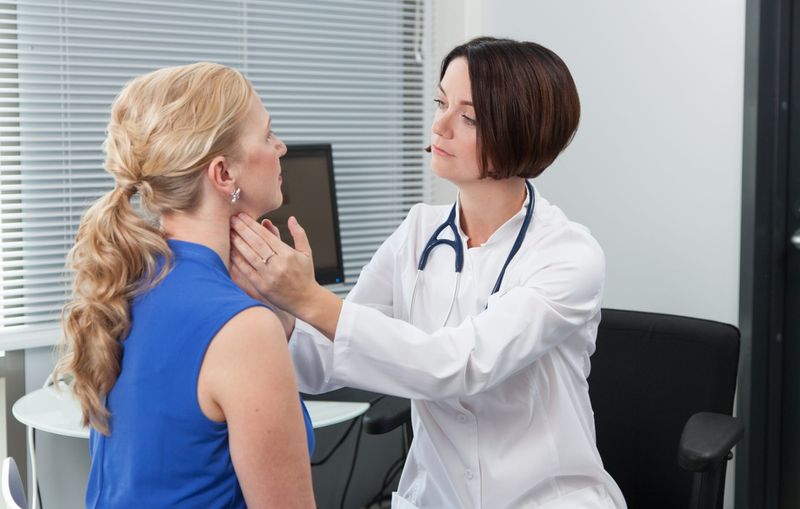
See your doctor if you have any unusual signs in your thyroid gland.
Treatment of Toxic Thyroid Adenoma
Treatment of Toxic Thyroid Adenoma depends on many factors, including: Size, type of thyroid nodule, age, health, risk factors for thyroid cancer. Here are some treatments for Toxic Thyroid Adenoma:
Antithyroid Medications
Antithyroid medications are the most common treatment for Toxic Thyroid Adenoma. These medications help reduce the production of thyroid hormones, thereby reducing the symptoms of hyperthyroidism. Antithyroid medications are usually used for 1-2 years to control the disease.
Thyroidectomy
Surgery to remove the thyroid gland is necessary if the thyroid nodule is large or has a high risk of becoming cancerous. This surgery is usually performed under general anesthesia and can be performed either by open surgery or laparoscopically.
In some cases, patients need to undergo thyroidectomy.
Radioactive iodine therapy
Radioactive iodine therapy is a treatment that uses radioactive iodine to destroy thyroid cells. This therapy is often used to treat small thyroid tumors or inoperable thyroid tumors.
So we have learned what symptoms toxic thyroid tumors often present. The survival prognosis of patients with toxic thyroid tumors is a treatable disease. With appropriate treatment, most patients can control the disease and live a healthy life. Hopefully this article will help you in the process of taking care of your health.





