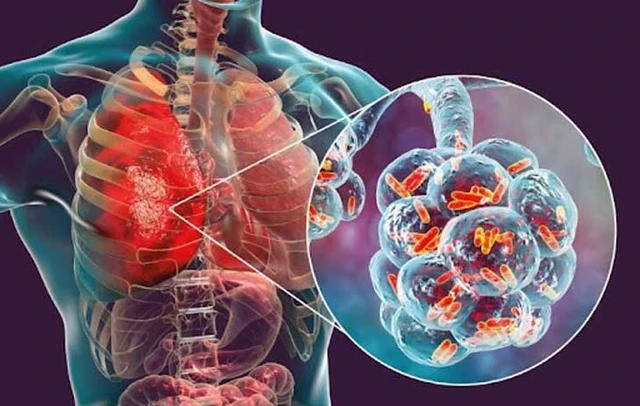
Staphylococcal pneumonia is often associated with influenza and measles outbreaks and is more common in people with chronic illnesses and immunodeficiency.
Many people believe that people infected with staphylococcus enter the lungs through breathing staphylococci into the respiratory tract, but staphylococci also come from skin infections that cause dermatitis and then pneumonia. Therefore, it is extremely important to pay attention to skin care to prevent staphylococcal pneumonia.
1. Overview of staphylococcal pneumonia
Staphylococcus is a Gram-positive coccus, when it has a capsule, staphylococci easily penetrate the blood causing sepsis. Staphylococcal pneumonia due to aspiration often occurs after influenza or in immunocompromised subjects, staphylococci are aspirated into the lungs through upper respiratory secretions.
The second mechanism is that staphylococci follow the blood to the lungs from extrapulmonary infections. According to this mechanism, pneumonia has many foci, often occurring in patients with dialysis, people with infected intravascular devices, thrombophlebitis, and tricuspid valve endocarditis.
And especially skin infections, boils caused by staphylococcus, especially on the face, can be complicated by pneumonia. When pneumonia appears, the boils on the skin may have already healed.
Staphylococcal pneumonia has an acute or subacute course. Clinical symptoms depend on the age and health of the patient. Pneumonia occurs very quickly after staphylococcal infections of the upper respiratory tract. When pneumonia is complicated, the symptoms of flu or measles are often worse.
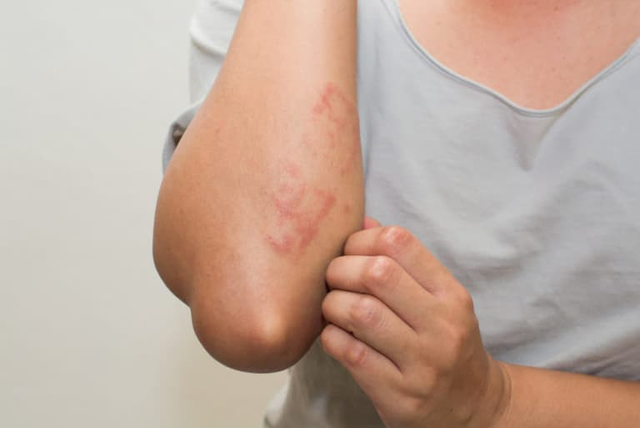
Staphylococcal dermatitis can occur in anyone.
2. Staphylococcal pneumonia from skin infections
A “gateway” that can be the entrance for many types of bacteria that cause pneumonia that few people pay attention to is the skin. In fact, many people with severe pneumonia have died due to not being treated early for causes originating from skin lesions.
There are many types of microorganisms that parasitize the skin of normal people, including bacteria that can be very dangerous to life such as staphylococcus aureus. If this bacteria enters the blood and moves to the lungs, it can cause pneumonia with a mortality rate of up to 30%.
Researchers say that people who are susceptible to staphylococcal pneumonia are: people with poor living conditions, poor hygiene, people who have the habit of using antibiotics indiscriminately, and patients who have been hospitalized for a long time. Living in poverty reduces resistance, along with poor hygiene conditions, making it easy to get dermatitis, boils caused by staphylococci, which in turn can easily get staphylococcal pneumonia through the bloodstream.
Staphylococci secrete many toxins and extracellular enzymes. They can also create polysaccharide shells that resist phagocytes. When they have a shell, staphylococci invade the bloodstream, causing septicemia. Staphylococci without a shell mainly cause local disease, but when they enter the bloodstream through intravenous injection, they often cause septic shock.
Causes that can weaken the skin’s defense mechanism include: Not bathing to remove dead skin layers, not taking good care of skin wounds, causing loss of physical barriers; leaving the skin dehydrated, not having enough secretions to chemically kill bacteria; not having enough micronutrients for immune cells to function biologically, etc.
In humid, hot weather, if there is a lack of water for daily use and poor personal hygiene, staphylococcal diseases are more likely to develop.
3. Symptoms of staphylococcal pneumonia from skin infections
First of all, based on the epidemiological characteristics of the history of skin boils (usually cured), clinical symptoms. In fact, skin and mucosal infections caused by staphylococci are a common disease in the hot season, especially boils, impetigo, and skin ulcers.
When infected areas on the skin sometimes form abscesses located right under the skin, causing pain, fever, swelling, and congestion, making the entire skin area red.
In infants and young children, if infected with staphylococcus, it can cause neonatal dermatitis or peeling skin syndrome in young children. The disease is manifested by the appearance of the epidermis immediately after fever and redness, and blisters forming over a fairly large area of skin.
Dermatitis can also form small abscesses like pinheads on the scalp due to inflammation and blockage of hair follicles, sweat glands, and sebaceous glands. Many cases of inflammation form boils (abscesses) on the scalp that burst due to various causes, causing the secretion of plasma and staphylococcus bacteria to spread to other areas of the skin and cause disease.
Especially in hairy areas such as the head (children and adults), armpits, pubic area (adults). Staphylococcus also causes boils (beard boils), an acute bacterial infection that can be life-threatening because of the high risk of causing septicemia.
Staphylococcus causes diseases in organs deep in the body such as diaphragmatic abscesses, thigh and calf muscle abscesses, lung abscesses. Diseases caused by staphylococcus on the skin and mucous membranes can be exogenous (the external environment enters the body and causes disease) but can also be endogenous (staphylococcus bacteria are present in the body, when favorable conditions arise, they become pathogenic, because up to 20 – 30% of healthy people carry this bacteria on the skin and mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract).
Therefore, in humid, hot weather, if there is a lack of water for daily activities and poor personal hygiene, staphylococcal diseases are more likely to develop and sometimes cause family epidemics.
4. Pay attention to clean skin to prevent staphylococcal pneumonia
To avoid staphylococcal pneumonia, we need to create conditions for all protective mechanisms to work effectively. In addition to strengthening the body’s resistance by exercising, drinking enough water, maintaining a nutritious diet, supplementing vitamins and trace elements, etc., proper skin care also plays an important role, contributing to improving the skin’s resistance.
This not only helps prevent skin diseases caused by staphylococcal infections (such as boils, dermatitis, folliculitis, etc.) but also prevents some internal diseases including pneumonia. In addition, healthy skin resistance also helps protect the body better from viruses and bacteria that cause disease, especially when the epidemic is still dangerous like now.
To limit the risk of getting sick, especially in humid, hot weather caused by staphylococcus, it is necessary to practice good personal hygiene by bathing and washing daily with clean water, especially for chubby children with many folds and folds containing a lot of sweat and sebum.
It is necessary to clean the throat and mouth every day by brushing teeth and gargling with light salt water before going to bed and after waking up. Every time you go out, you should wear a mask to avoid inhaling dust. If you have a respiratory infection, especially upper respiratory diseases (rhinitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis), you need to treat it completely, do not let it become a chronic disease.





