The immune system of infants and young children is still weak and incomplete, making them susceptible to disease. So, what are the common diseases in children that parents should know to prevent?
The health and development of children is always the top priority of parents. To better protect and care for infants, recognizing and understanding common diseases in children is extremely important. This helps parents feel more confident in dealing with their children’s health situations.
How do diseases affect children’s development?
Diseases significantly affect children’s health and development in many aspects. Physically, they hinder growth and motor skill development, causing children to slow down in reaching important developmental milestones. Children who are sick for a long time are often tired, have reduced activity, affecting their overall health.
Mentally, illness causes stress, discomfort, affects the child’s ability to concentrate, learn and regulate emotions. Society is also affected when children often have to miss school, making it difficult to integrate with friends, making them feel isolated. In addition, children can develop neurological and motor sequelae, affecting the future.
Common diseases in children
Below are some common diseases in children that can affect the health and development of children.
Cold
Cold is a common respiratory disease caused by Rhinovirus or Enterovirus. The disease can be transmitted from person to person and often breaks out when the weather changes. Symptoms are usually mild and go away on their own after 3 – 7 days if properly cared for. However, colds can also cause dangerous complications such as ear infections, sinus infections, or pneumonia. The risk of recurrence can also occur after complete treatment.
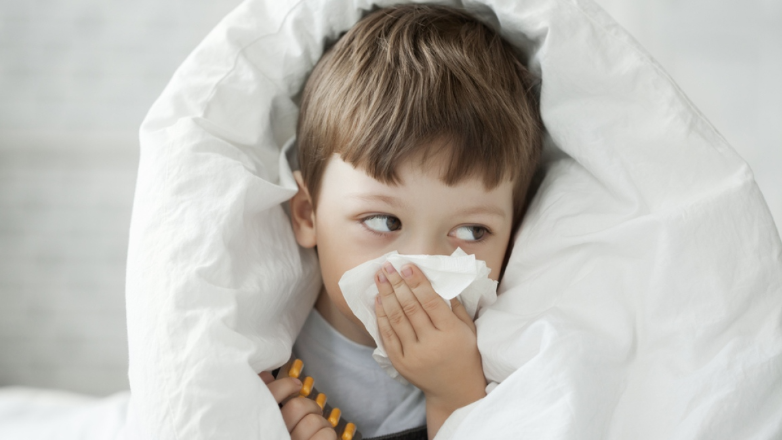

Colds are one of the most common illnesses in children.
Ear Infections
Ear infections (otitis media) can be caused by bacteria or viruses. Symptoms include earache, fever, irritability, sleeplessness, loss of appetite, ear twitching and hearing loss. Children are at higher risk because their Eustachian tubes are shorter but have a larger diameter, making it easier for bacteria to enter and cause inflammation and infection.
Influenza
Influenza is a common childhood illness caused by a virus that is spread through direct contact with droplets from an infected person when they sneeze or talk. Symptoms include fever, sore throat, fatigue, muscle aches and chills. Regular flu vaccination can reduce the risk and severity of the disease.
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is the leading cause of death in children under 5 years of age, with about 2.9 million children affected each year in Vietnam. Caused by the bacteria Streptococcus pneumoniae, the disease can lead to serious complications such as sepsis and meningitis if not treated promptly.
Diphtheria
Diphtheria causes pseudomembranes in the throat, which can cause many complications if left untreated.
Children may suffer from respiratory failure, circulatory failure, paralysis of the tongue, confusion, coma, and even death if not detected and treated promptly.
Bronchitis
Bronchitis often occurs in children from 6 months to 3 years old, especially in cold weather. Viruses are the main cause, but other factors such as allergies and environmental pollution also contribute. Symptoms include runny nose, difficulty breathing, dry cough, fever, and fatigue.
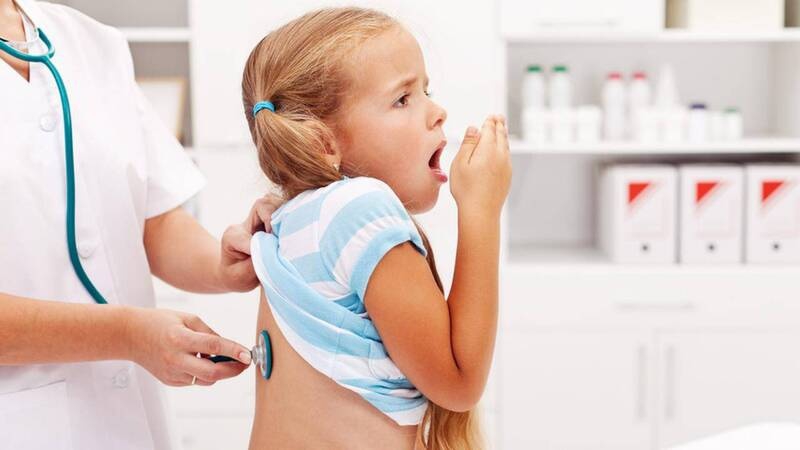

Bronchitis often occurs in children from 6 months to 3 years old.
RSV
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) commonly causes respiratory infections in young children, especially infants under 6 months of age. Symptoms include fever, cough, runny nose, and sneezing, similar to a cold. RSV often flares up in cold weather and can cause dangerous, life-threatening complications for children.
Gastroenteritis
Gastroenteritis (stomach flu) is a flu-like illness caused by a virus, with symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. The illness usually goes away on its own after a few days with rest and proper care.
Sinusitis
Sinusitis is a condition in which fluid builds up in the sinuses, usually caused by a virus, with symptoms such as nasal congestion, runny nose, headache, pressure in the sinus area, and sore throat. Pharyngitis is caused by the bacteria streptococcus pyogenes, and often occurs during seasonal changes.
Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis in children is a disease caused by the invasion of streptococcus pyogenes bacteria into the nose and throat. The disease often occurs during the transition from autumn to winter. Children with the disease often have sore throats, fever, swollen tonsils and stomach pain.
Hand, foot and mouth disease
Is an infectious disease caused by coxsackievirus A16 or enterovirus 71, common in children under 5 years old with symptoms such as rash, high fever, mouth ulcers and flu-like symptoms.
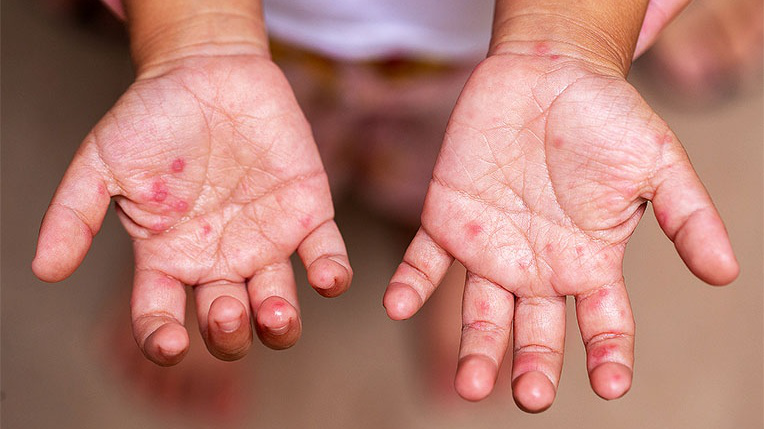
Hand, foot and mouth disease is caused by coxsackievirus A16 or enterovirus 71.
Skin Infections
Skin infections can cause mild to severe skin lesions. Common symptoms of this disease in children include boils, impetigo, and intertrigo.
Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections are common in girls and can cause symptoms such as lower abdominal pain, frequent urination, and loss of bladder control.
Diarrhea
Loose stools are common in children and can be caused by bacterial, viral, or parasitic infections. There are many causes of diarrhea in children, including bacteria, viruses, parasites, or gastrointestinal diseases.
Acute Diarrhea Due to Rotavirus
The disease occurs mostly in children under 5 years old, especially children under 2 years old. Acute diarrhea due to Rotavirus usually resolves on its own after 5-7 days, but attention should be paid to treating symptoms and preventing dehydration.
Chickenpox
Chickenpox is a disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus, which can be spread through direct contact or through secretions from an infected person. Symptoms usually last 5 to 10 days and include itchy red blisters. They usually do not cause complications, but can cause skin infections or shingles.

Chickenpox is quite common in children.
Cough
Cough is a reaction of the body, which can be caused by many different reasons, so you should take your child to the doctor for examination and proper treatment.
Measles
Measles is a viral disease transmitted through the respiratory tract, with symptoms such as fever, conjunctivitis and rash all over the body, which can cause serious complications such as encephalitis, corneal ulcers, pneumonia, otitis media, etc.
Japanese encephalitis
Japanese encephalitis, caused by the JEV virus transmitted through mosquito bites, can cause death and complications in children, especially those under 4 years old. There is currently no specific treatment for this disease.
Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis often occurs during the changing seasons, usually caused by Adenovirus or streptococcus. The changing seasons, heavy rain, and humidity are the times when the disease most often occurs.
Tetus
Tetus is caused by the toxin Clostridium tetani, which can cause death and damage to the nervous system. On average, up to 500,000 children die from tetanus each year in developing countries.
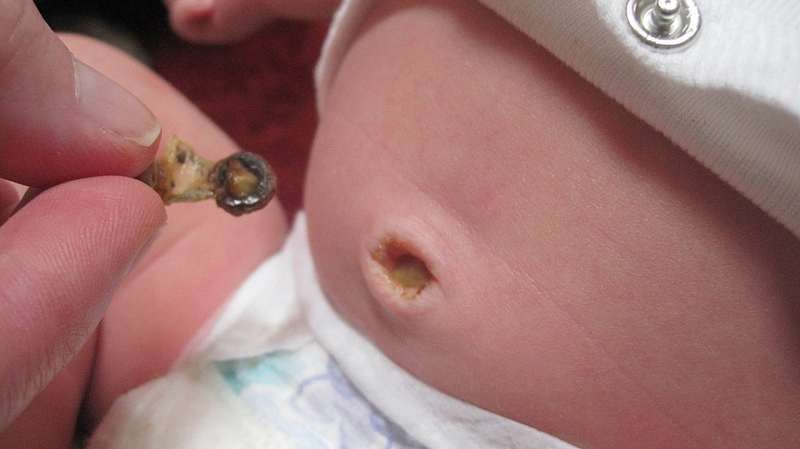
Tetanus caused by Clostridium tetani toxin
Dengue fever
Dengue fever caused by the Dengue virus can cause fever, headache and bleeding from various organs. Initial symptoms such as fever, rash, headache, body aches, bleeding gums, nosebleeds are common.
Worm infection
Worm infection is common in children and can cause many serious health problems. Abdominal pain, nausea, loss of appetite, heartburn and diarrhea are common symptoms.
Hepatitis
Hepatitis, which damages the liver, can cause fatigue, jaundice and other problems. Children with the disease have symptoms of fatigue, abdominal pain, headache, loss of appetite, weight loss, vomiting, jaundice, etc.
How to prevent diseases in children
To protect children from common diseases, parents need to note the following:
- Have children wash their hands regularly to prevent infection.
- Ensure a balanced diet and adequate water.
- Ensure personal hygiene for children and educate them about healthy habits.
- Get your children vaccinated on schedule to reduce the risk of dangerous diseases.
- Limit contact with sick people and crowded places during epidemics.
- Encourage children to exercise regularly to increase their resistance.
- Keep the living environment clean by cleaning and disinfecting regularly.
Understanding and preventing common diseases in children is extremely important. With proper care and effective preventive measures, we can help protect children’s health, reduce the risk of disease and create conditions for their comprehensive development.





