Vision is the most important of the body’s five senses. Eye health goes hand in hand with overall health, so a special diet for the eyes is needed.
1. The importance of diet for people with optic nerve atrophy
Optic nerve atrophy is a condition in which the optic nerve is damaged due to any cause, limiting the ability to transmit information from the eye to the brain. Symptoms of optic nerve atrophy are often: decreased vision, decreased ability to perceive colors and eye pain when moving.
The consequences of the disease affect both distance vision, near vision and the ability to perceive colors of the eye, and can eventually lead to blindness if optic nerve atrophy is not treated. Older people often have optic nerve atrophy due to reduced blood flow to the optic nerve.
Optic nerve atrophy accounts for about 0.8% of the causes of blindness. This is not a disease but a consequence of many different diseases.
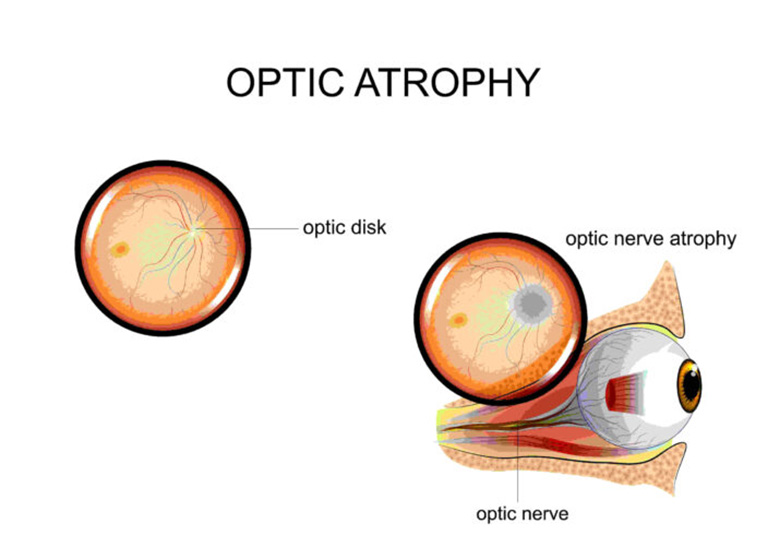
Optic nerve atrophy is a condition of damage to the optic nerve that causes vision loss.
Although diet cannot cure the disease, it plays an important role in supporting the treatment process. At the same time, it reduces symptoms and minimizes serious problems caused by the disease. Building a reasonable diet provides necessary nutrition and helps strengthen health, fight against the disease.
2. Essential nutrients for the body of people with optic nerve atrophy
- Vitamin A: Vitamin A deficiency is one of the most common causes of vision loss. This vitamin plays an important role in maintaining light-sensing cells in the eye, also known as photoreceptors. If the body does not have enough vitamin A, we may suffer from night blindness, dry eyes or more serious eye diseases, depending on the level of deficiency.
- Lutein and zeaxanthin: are antioxidants, these two substances are often concentrated in the central part of the retina. They act as a natural sunscreen, protecting the eyes from the harmful effects of sunlight. In addition, these substances also help absorb blue light (a dangerous type of light emitted from electronic screens) that is dangerous to the retina.

Most red fruits and vegetables are good for eye health and tomatoes are one of them.
- Vitamin C: The eyes require high levels of antioxidants, and more so than other organs in the body. Vitamin C is an especially important antioxidant for the eyes. The concentration of vitamin C in the eyes is much higher than that in any other fluid in the body.
- Vitamin E: belongs to a group of fat-soluble antioxidants that protect fatty acids from harmful oxidation. Because the retina has a high concentration of fatty acids, vitamin E is essential for eye health.
- Long-chain omega-3 fatty acids such as eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) are important for eye health. DHA is found in large amounts in the retina, where it helps maintain eye function. This fatty acid is also important for brain and eye development during infancy. DHA deficiency can lead to impaired vision, especially in children. In addition, regular omega-3 supplementation is also very beneficial for people with dry eye disease.
- Zinc is a component of many essential enzymes, including superoxide dismutase, which functions as an antioxidant. Zinc is involved in the formation of visual pigments in the retina, and zinc deficiency can lead to night blindness.
3. Suggested foods for people with optic nerve atrophy
According to modern nutrition, foods that are good for vision need to contain many substances such as: vitamin A, beta-carotene, vitamin C, vitamin E, lutein, selenium… Therefore, to nourish and protect the eyes’ function well and for a long time, we should regularly use the following foods:
Animal liver, cow’s milk, sheep’s milk, goat’s milk, egg yolks, fish liver oil… because these are foods rich in vitamin A. A lack of vitamin A in the body will cause night blindness, sometimes so severe that you cannot see clearly at night. Vitamin A deficiency also leads to dry eyes.

Beans, lean meat, peanuts, brown rice… these are foods rich in vitamin B1 and niacin.
- Green vegetables, white cabbage, spinach (purslane), rapeseed, green beans, pumpkin, tomatoes, carrots, apples, sweet potatoes, squash, papaya, especially gac fruit… these are foods that contain a lot of carotene. After eating, the body absorbs carotene and then converts it into vitamin A.
- Beans, lean meat, peanuts, brown rice (ie rice without husk), green leafy vegetables, green beans, apples, corn… These are foods rich in vitamin B1 and niacin. If there is a lack of vitamin B1, it will cause neuritis, especially the optic nerve, retinal hemorrhage, and rapid loss of vision… Niacin deficiency will cause nystagmus, weakening vision…
- Fish, shrimp, clams, milk, red apples, seaweed… are foods rich in phosphorus. Phosphorus plays a very important role in maintaining the elasticity of the sclera.
Besides, you also need to change your lifestyle such as: not working on the computer continuously for a long time, causing your eyesight to decrease, including: blurred vision, dry eyes, eye pain, eye fatigue, nearsightedness, astigmatism… or watching too much TV, reading too much, incorrect posture, distance… will cause many eye problems, especially nearsightedness.





