Follicular thyroid cancer occurs in the thyroid gland, which produces hormones that regulate metabolism. This is a potentially curable form of thyroid cancer. Let’s learn more about the effects, risk factors, and treatments for follicular thyroid cancer in the article below.
What is follicular thyroid cancer?
Follicular thyroid cancer is a common form of differentiated thyroid cancer (after papillary thyroid cancer), accounting for about 10 – 15% of all thyroid cancer cases. This cancer originates from the abnormal growth of follicular cells in the thyroid gland. Physiologically, the thyroid gland is an important endocrine organ responsible for hormone production. The structure of the thyroid gland includes thyroid follicles, which play an important role in maintaining the body’s metabolic function by using iodine from the blood to produce thyroid hormones.
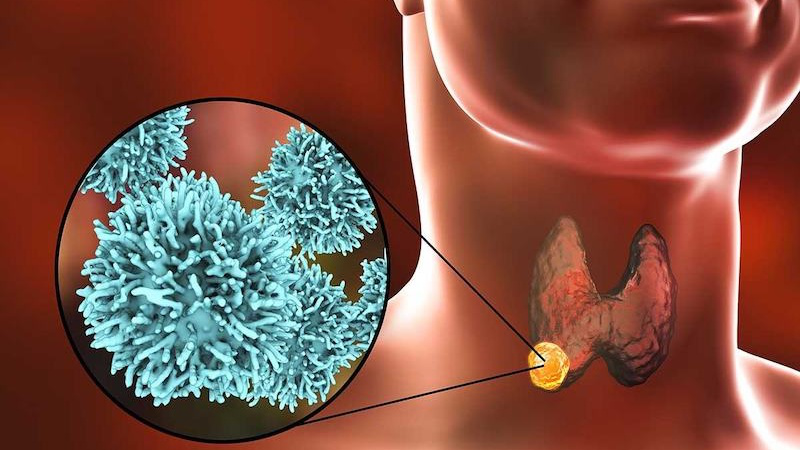
Follicular thyroid cancer accounts for about 10 – 15% of all thyroid cancer cases.
Signs and effects of follicular thyroid cancer
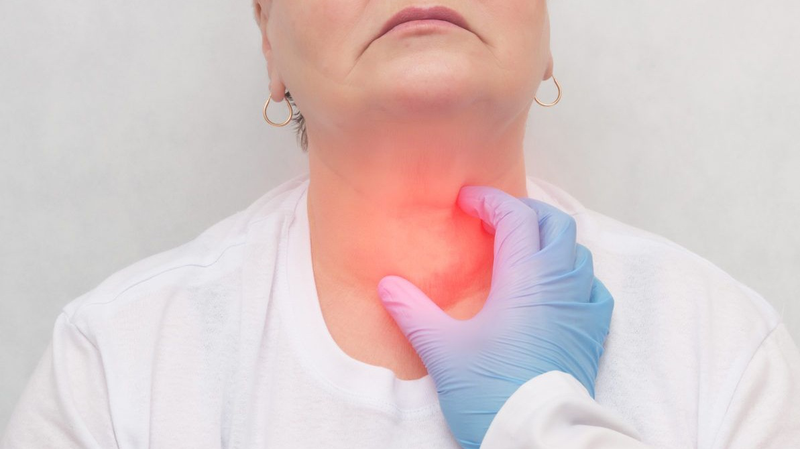
Follicular thyroid cancer can lead to the appearance of a lump or pain in the neck. If the disease is diagnosed in the early stages, the possibility of successful treatment is high. On the contrary, if not treated promptly, the cancer can spread to other parts of the body. In the case of follicular thyroid cancer in the metastatic stage, treatment becomes more difficult.
Recognizing the disease through symptoms and signs can be difficult to determine. Because follicular thyroid cancer may not cause any symptoms or may vary depending on each patient. However, some signs that you can recognize include:
- The appearance of a lump in the neck;
- Earache, jaw pain or neck pain;
- Hoarseness (difficulty speaking);
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck;
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing.
Who is at risk for follicular thyroid cancer?
People with the following characteristics are at increased risk of developing follicular thyroid cancer:
- Being 50 years of age or older, rare in children and adolescents.
- Women are more likely to develop the disease than men.
- People with a history of radiation therapy in the past.
- Family history of thyroid cancer syndromes, especially in first-degree relatives (parents).
- People with diabetes or thyroid-related diseases.
- People who are overweight or obese.
- Dietary iodine deficiency.
People over 50 years old have a high risk of developing papillary thyroid cancer.
How is follicular thyroid cancer treated?
The approach to treatment for follicular thyroid cancer depends on the stage of the disease and the patient’s specific health condition. Here are some treatments for follicular thyroid cancer:
Thyroid surgery
The main treatment for patients with follicular thyroid cancer includes surgery to remove part or all of the thyroid gland (lobectomy/isthmusectomy or total thyroidectomy), with or without neck dissection. The decision to choose between partial or total thyroidectomy depends on many factors such as the characteristics of the tumor, the extent of metastasis, and the patient’s preferences.
Patients who choose total thyroidectomy will usually be treated with thyroid hormone medication for the rest of their lives. Thyroid surgery should be performed by experienced doctors to minimize the risk of complications, such as laryngeal nerve damage and hypoparathyroidism.
Radioactive Iodine Therapy
After total thyroidectomy, the physician will evaluate several factors to determine whether radioactive iodine therapy is necessary. Clinical and pathologic factors used to make the decision include tumor size, extent of invasion, lymph node metastasis, vascular invasion, and postoperative Tg (thyroglobulin) levels. The dose of radioactive iodine is determined based on the patient’s specific risks.

Radioactive iodine therapy after total thyroidectomy
Other methods
In cases where after initial treatment, the patient relapses, progresses, metastasizes, or does not respond positively to radioactive iodine treatment, the doctor may decide to use other treatments such as:
- Targeted therapy: Using drugs such as lenvatinib, sorafenib, and other options that target the growth mechanism of cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: Using drugs such as pembrolizumab to stimulate the immune system and help the body fight against cancer cells.
- Local treatment (external radiation therapy): Applying radiation therapy from a distance to destroy or control cancer cells where they grow.
The decision about the treatment method will depend on the patient’s specific health condition and cancer condition.
Follicular thyroid cancer is a serious disease that can affect the patient’s quality of life and overall health. Being well informed about risk factors, symptoms, and treatments is essential to ensure early diagnosis and intervention, thereby optimizing treatment outcomes.





