Cataracts are commonly known as dry cataracts, stone cataracts, granular cataracts or cataracts. The disease is common in people over 50 years old. This is a dangerous disease that can lead to blindness and greatly affects the patient’s quality of life.
Cataract is always one of the leading causes of vision loss and blindness in the world. This is a slow-progressing disease, initially manifested by a decrease in the power of reading glasses; when looking at the light, the eyes will be uncomfortable. Then the disease will get worse, the eyes feel like looking through a layer of frosted glass, can see a fixed black spot; gradually the patient will lose vision.
1. What is cataract?
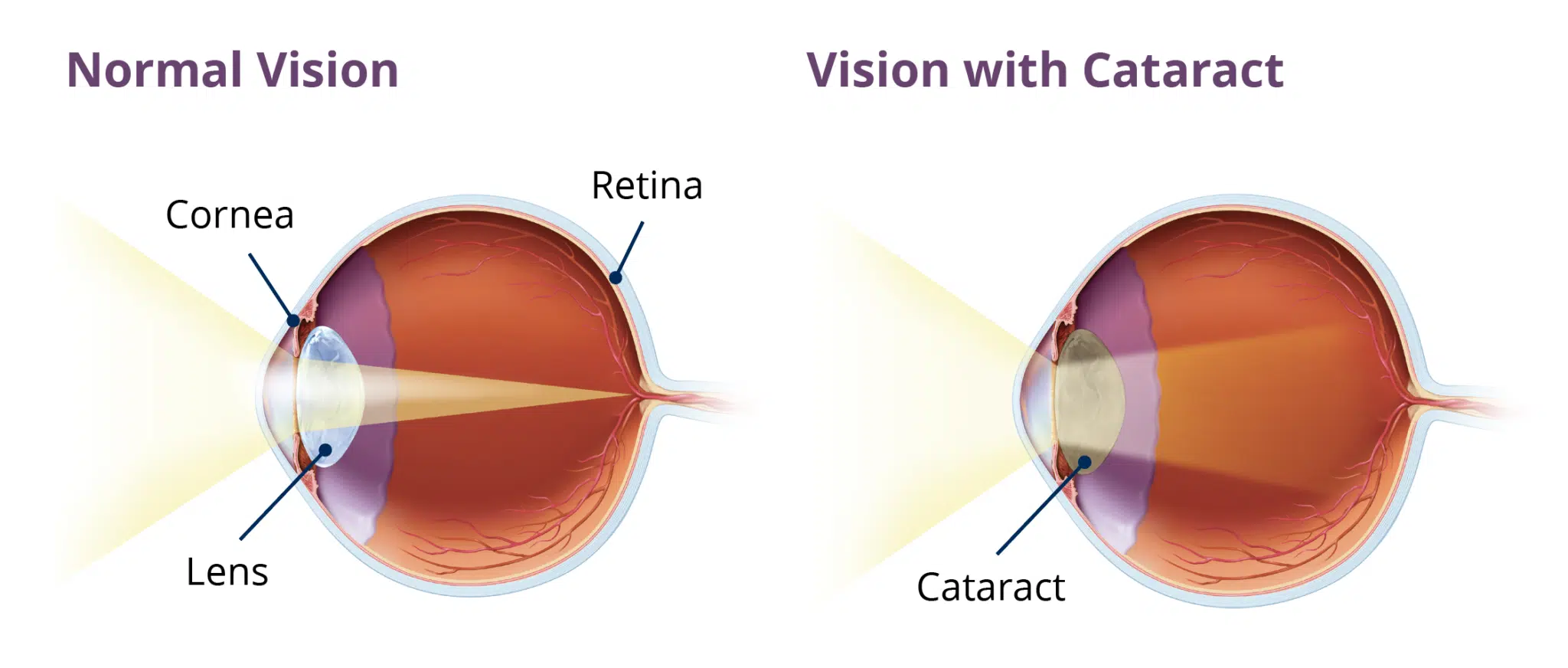
The lens is a transparent, biconvex lens. This is an important component that helps light pass through, helping light rays converge correctly on the retina.
It can be seen that the converging power of the lens plays an important role in the refractive system, helping the focal point of the image converge correctly on the retina when looking far away. The thickness of the lens will help the eye adjust to see objects clearly near.
Over time, the transparent lens will become less transparent, the lens will become opaque, making it difficult for light to pass through, causing the patient to gradually lose vision, see everything blurry, and even cause blindness. Cataracts can occur in different layers of the lens such as: Central nucleus (nuclear cataract); under the posterior lens capsule (posterior subcapsular cataract) or lens cortex cataract (will not cause vision loss)
2. Causes of cataracts
2.1 Primary causes
Can be congenital related to disorders with genetic factors. In addition, the disease can also arise due to the mother having infectious diseases such as syphilis, measles during pregnancy, etc.
Due to age and the natural aging process, it can affect the nutrition of the lens. Therefore, the disease is common in people over 50 years old.
2.2 Secondary causes
– Due to diseases such as diabetes, glaucoma or obesity… Long-term use of certain drugs such as lipid-lowering drugs, corticosteroids, drugs to treat depression, arrhythmias, etc. also increases the risk of cataracts.
– Eye injuries: There are some eye injuries that can lead to cataracts.
– Regular exposure to sunlight, X-rays, welding light…
2.3 Related factors
– Due to aging, the eyes are not cared for, exercised and provided with nutrients for the eyes.
– Regular use of stimulants such as beer, alcohol, cigarettes…
– Insomnia, stress and frequent exposure to polluted environments.
3. Signs of cataracts
Cataracts develop slowly and silently, causing no pain to the patient. In the early stages, there are almost no signs of the disease. When the disease progresses, the following symptoms will appear:
– Eyes see everything blurry, or ache when focusing on an object. Vision gradually declines, this is the first and most important symptom of the disease.
– Eyes will be more sensitive to light, eyes may be dazzled. It may be more difficult to see bright areas in shaded areas.
– Often seeing double, seeing one object as multiple objects, seeing as if there is a fog covering the eyes… These symptoms can be seen in one eye or both eyes.

Blurred vision is the most important symptom of cataracts.
4. Diagnosis of cataracts
To detect the disease, it is necessary to examine the fundus and use a slit lamp. It is best to diagnose when the pupil is dilated. Progressive cataracts appear as gray, white or yellow-brown opacities. Evaluating the pupillary reflex through a dilated pupil with a slit lamp will reveal the types of cataracts. A slit lamp examination provides information about the characteristics, location and degree of opacity of the lens.
5. Treatment of cataracts
– The disease can cause blindness, so it needs to be detected and treated promptly. Currently, it is very difficult to make the lens clear again. In patients who have just started to have the disease and do not need surgery, doctors will prescribe some vitamins such as C, A, E … and some other active ingredients to slow down the progression of cataracts.
– Until now, the most effective treatment method is still surgery. Phacoemusification surgery (Phaco surgery) is increasingly popular and is currently the best treatment method. The advantages of this surgical method are small incisions and quick recovery of vision, rare complications and patients can quickly recover to normal. Phaco surgeries only last about 5 to 10 minutes, however, this is classified as a major surgery because it is a surgery that directly affects vision. Phaco surgery uses the smallest incision so the incision heals quickly and this is the preferred choice of many surgeons. Femtosecond laser can be used in refractive cataract surgery to perform some stages before phacoemulsification. In extracapsular cataract surgery (including phaco), the lens capsule is preserved.
– Cases where doctors prescribe conventional surgery when: Maximum visual acuity with glasses is worse than 20/40 (< 6/12), or visual acuity is reduced in bright light conditions, in patients with colored halos; when the patient’s vision rapidly decreases, hindering daily activities such as driving, reading, walking, etc.; The patient’s vision can improve significantly after surgery (ie, there is a decrease in vision due to cataracts).
– Other less common indications are when cataracts cause glaucoma or obstruct vision. Patients need regular eye examinations to detect chronic diseases: diabetic retinopathy or macular degeneration, etc.
6. Postoperative care and postoperative complications
In most cases, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics and topical corticosteroids for 4 weeks after surgery. Pre-operative antibiotics can be injected at the end of surgery to help reduce complications of endophthalmitis. Patients are often instructed to cover their eyes when sleeping; avoid coughing, lifting heavy objects, and limit rubbing their eyes, etc.
Complications after cataract surgery are very rare. There may be complications such as:
- During surgery: subretinal hemorrhage, intraocular entrapment in the surgical wound – very rare and causing irreversible vision loss, nuclear fragments falling into the vitreous chamber, vitreous entrapment, corneal endothelial detachment…
- In the first week: endophthalmitis, glaucoma… may occur, however, this is very rare.
- Macular edema in the first month after surgery
- Retinal detachment, and posterior capsular opacification… may occur a few months after surgery but can be treated with laser
7. Prevention of cataracts

Regularly supplement vitamins C, E, A, lutein, zinc zeaxanthin found in green vegetables and fruits.
– Regular eye examinations help detect eye diseases and cataracts early
- Control and treat diabetes early. Have a regular diet and exercise to avoid eye complications. Detect and treat diseases such as uveitis, glaucoma early…
- Build a healthy diet. Supplement antioxidants and improve liver function to prevent disease. Regularly supplement vitamins C, E, A, lutein, zinc zeaxanthin found in green vegetables, fruits, fish, cereals… Limit fried foods, greasy foods, sweets, etc.
– In addition, increase the lighting in the house, avoid direct exposure to sunlight and dust. When going out, wear glasses and a hat to protect your eyes. Establish a reasonable scientific lifestyle, do not smoke, limit alcohol.





