In this article, we will explore in detail the structure, function, and health problems associated with the thyroid cartilage. From common disorders like thyroid cartilage inflammation to treatments and care, let’s take a closer look at this fascinating part of the human body.
Understanding Thyroid Cartilage
The thyroid cartilage, also known as the thyroid cartilage, is the largest of the cartilages that make up the larynx. The thyroid cartilage plays an important role in the structure of the larynx, in addition to contributing to the role of the respiratory and digestive systems in the body.
Location, structure of the thyroid cartilage
The location of the thyroid cartilage is very recognizable, it is located just under the skin in the front part of the neck, above the cricoid cartilage and below the diaphragm. The thyroid cartilage is connected to the vocal and cricoid cartilages through ligaments and muscles, creating a complex and flexible structure.
The thyroid cartilage is composed mainly of hyaline cartilage, a tough and durable cartilage that helps maintain the shape and structure necessary for the larynx. The shape of the thyroid cartilage resembles a shield or shield, consisting of two flat quadrilateral cartilage plates that join together in the front of the neck and extend backward.
The interesting thing about the thyroid cartilage is that the angle of this angle differs between men and women. In men, this angle is about 90 degrees, creating a distinct square shape. The formation of this right angle results in a forward projection of the thyroid cartilage. In contrast, in women, this angle of the thyroid cartilage is more obtuse, about 120 degrees. Therefore, the shape of the thyroid cartilage in women does not create a clear projection as in men. This difference not only creates a distinct anatomical feature between the two sexes, but also affects the function of the thyroid cartilage in protecting the vocal cords and assisting in the swallowing process.
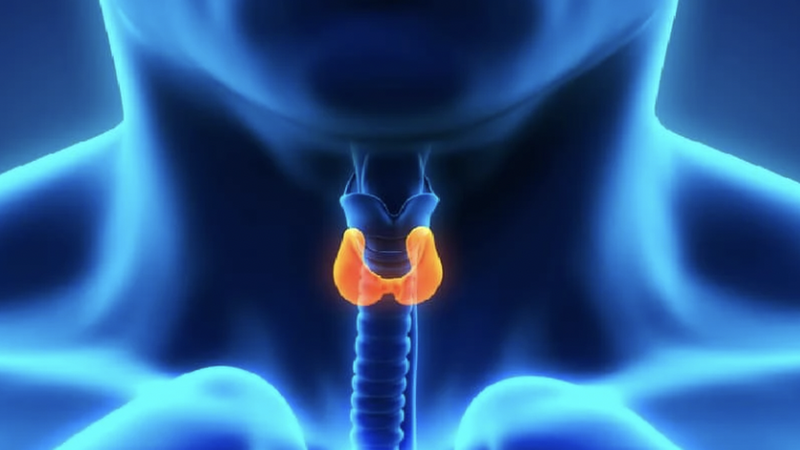
Thyroid cartilage plays an important role in the respiratory and digestive systems.
Functions of the thyroid cartilage
In the respiratory system, the thyroid cartilage plays an essential role in protecting the vocal cords and trachea, thereby directly affecting the ability to speak and breathe.
In addition, the thyroid cartilage also supports the swallowing process and protects the respiratory tract from the invasion of food or liquid. When swallowing, the thyroid cartilage and the entire larynx lift up to help close the entrance to the trachea, preventing food or water from the mouth and throat from falling into the lungs. This process not only protects the airway from foreign objects but also ensures that food is moved in the right direction into the esophagus, leading to the stomach. This is extremely important, because the invasion of food or liquid into the lungs not only causes coughing or choking but can also lead to dangerous conditions such as aspiration pneumonia.

Thyroid cartilage helps support the swallowing process when eating.
In addition, the thyroid cartilage also plays a role in protecting the vocal cords. The vocal cords, located in the larynx, are the main structures that produce sound when we speak or sing. The thyroid cartilage, through its structure and location, helps protect the vocal cords from damage or foreign objects, while maintaining their flexibility.
Disorders and diseases related to the thyroid cartilage
Thyroid cartilage inflammation
Thyroid cartilage inflammation is a serious medical condition, related to infection. Symptoms of thyroid cartilage inflammation are often very obvious and can cause significant pain and discomfort for the patient. The main symptoms include pain in the neck area, especially in the front part, where the thyroid cartilage is located. The pain may increase when swallowing or when touching that area. Swelling and inflammation of the thyroid cartilage can make swallowing difficult and painful. Coughing may occur due to irritation of the upper respiratory tract or due to mucus accumulation. In severe cases, swelling and inflammation can cause difficulty breathing.
The most common cause of thyroiditis is a bacterial infection. Infections can occur for many reasons, including spreading infection from other parts of the body, from neck injuries, or after medical procedures such as laryngoscopy. In some cases, thyroiditis can also develop from an autoimmune reaction, which means the body mistakenly attacks healthy cells.

Thyroiditis is a serious condition that is mainly caused by infection.
Thyroid Cartilage Tumors
Thyroid cartilage tumors are a complex medical condition that can include benign or malignant tumors. The presence of tumors in this area can significantly affect the structure and function of the thyroid cartilage, as well as the surrounding structures of the respiratory system and larynx.
Benign tumors are harmless, slow-growing cartilaginous masses that do not spread to surrounding tissues. Benign tumors usually cause no symptoms or only mild symptoms such as discomfort or slight swelling in the neck. They rarely interfere with breathing or swallowing unless the tumor is large enough to put pressure on nearby structures.
Malignant thyroid cartilage tumors are a serious medical condition that requires immediate treatment. Malignant tumors often grow rapidly and have the potential to invade nearby tissues and structures. Symptoms of a malignant tumor may include neck pain, difficulty swallowing, voice changes, unexplained cough, and in some cases, difficulty breathing. The growth of the tumor can put pressure on the airway and vocal cords, making it difficult to breathe and speak.
Thyroid Cartilage Treatment and Care
Thyroid cartilage, although not a common problem, needs careful treatment and care when it is disturbed or diseased. Modern medical treatments, as well as advice on daily care, can help maintain the health of the thyroid cartilage.
Medical Treatments
- Medical Treatment: For conditions such as thyroid cartilage inflammation, treatment usually begins with antibiotics. In some cases, corticosteroids are also used to reduce inflammation and swelling.
- Surgery: In cases of severe damage or deformity due to an accident, surgery may be necessary to repair or reconstruct the thyroid cartilage. Surgical procedures are also used for tumors on the thyroid cartilage.
- Postoperative management: After surgery, management and rehabilitation are important. Physical therapy exercises may be recommended to improve swallowing and speech function.
Surgery is required in cases of severe damage to the thyroid cartilage.
Tips for caring for your thyroid cartilage
- Keep your throat clean: Avoid smoking and exposure to smoke, keep your throat moist by drinking enough water, and use a humidifier when necessary.
- A balanced diet: A diet rich in vitamins and minerals, especially vitamin C and calcium, can help maintain healthy cartilage.
- Protect your neck when participating in sports: Use a neck brace when playing sports that have a high risk of neck injury.
- Regular health check-ups: People with a history of thyroid cartilage problems should have regular check-ups with a specialist.
The thyroid cartilage is an important part of the larynx structure, playing an essential role in protecting the vocal cords and airways, and supporting the swallowing process. Thyroid cartilage-related diseases such as inflammation, accidental damage, or tumor growth can significantly affect health and quality of life. Therefore, timely recognition and treatment of thyroid cartilage-related problems is important to maintain the overall health of the respiratory system and larynx.





