Left lobe thyroid adenoma is a disease of the thyroid gland, an important endocrine gland of the body. Understanding this condition not only helps you prevent it effectively but also provides necessary information for the treatment and recovery process.
What is left lobe thyroid adenoma?
The thyroid is a small endocrine gland located in the neck, which functions to produce hormones that regulate many important activities of the body, including metabolism, growth and development. When a tumor appears, this function can be disrupted, leading to dangerous symptoms and complications.
Causes
Left lobe thyroid adenoma can develop due to many different causes, including genetic, environmental and lifestyle factors. Genetically, if someone in the family has had thyroid-related diseases, your risk of developing this disease will also be higher.
In addition, a polluted living environment, especially exposure to radioactive substances or toxic chemicals, can increase the risk of the disease. Unhealthy lifestyles, including a diet low in iodine, smoking, alcohol use, and prolonged stress, also contribute to the development of thyroid tumors. These factors can directly or indirectly affect the thyroid gland, causing abnormalities in its structure and function.

Unhealthy lifestyle also contributes to the development of thyroid tumors.
Symptoms
Symptoms of left lobe thyroid tumors are often unclear in the early stages, but specific signs will gradually appear as the tumor grows. One of the first symptoms that can be noticed is swelling in the neck, where the thyroid gland is located. This can cause difficulty swallowing, a feeling of choking when eating and drinking. The tumor can also compress surrounding nerves and organs, leading to hoarseness or voice changes.
In addition, some patients may experience unexplained weight changes, usually rapid weight loss or difficulty controlling weight. These symptoms may be accompanied by a feeling of fatigue, weakness, and in some cases, pain in the neck or chest area. Early detection of these symptoms is very important for timely diagnosis and treatment, to prevent the development and complications of the disease.
Diagnosis and treatment of left lobe thyroid adenoma
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of left lobe thyroid adenoma usually begins with a physical examination, in which the doctor will examine the neck to detect any unusual swelling or lump. Then, to determine the exact condition of the thyroid gland, the doctor may order a number of imaging tests such as ultrasound, computed tomography (CT) scan and blood tests.
- Ultrasound is the most common method, helping to determine the size, location and nature of the tumor.
- CT scan provides more detailed images of the structure of the thyroid gland and surrounding organs, helping to detect small abnormalities that ultrasound may miss.
- Blood tests, including measuring thyroid hormone levels (TSH, T3, T4) and cancer markers such as calcitonin, thyroglobulin, help assess thyroid function and determine the tumor’s potential for cancer.
All of these methods combined give the doctor a comprehensive picture of the patient’s thyroid condition.
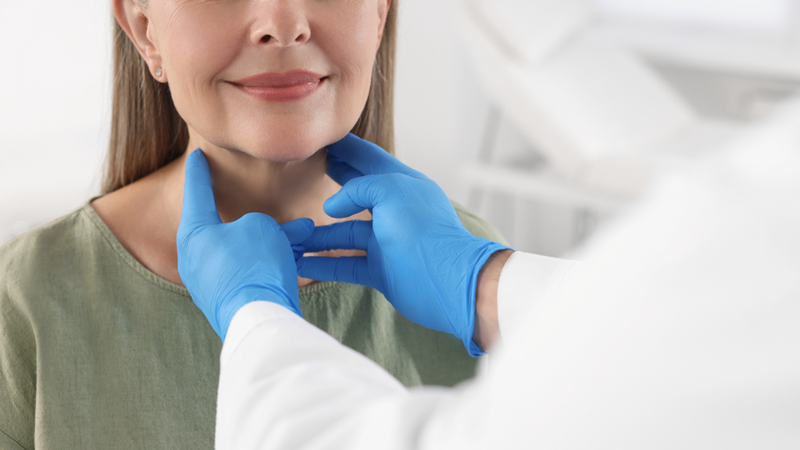
Diagnosis of left lobe thyroid adenoma usually begins with a clinical examination.
Treatment
Treatment of left lobe thyroid adenoma depends on the size, location, and nature of the tumor, as well as the patient’s general health. Surgery is the most common treatment, especially when the tumor is large or there are signs of suspected cancer. Surgery may include partial or total thyroidectomy, depending on how far the tumor has spread.
After surgery, the patient may need radiation therapy to destroy remaining cancer cells and prevent recurrence. Radiation therapy is often prescribed for cases of malignant or high-risk tumors.
In addition, hormone therapy also plays an important role in treatment, especially after total thyroidectomy. The patient will be supplemented with thyroid hormone to maintain the necessary hormone levels for the body and prevent symptoms of hypothyroidism.
Combining these treatments not only helps control the tumor but also improves the patient’s quality of life.
Impact of left lobe thyroid tumor on general health
Impact on the digestive system
Left lobe thyroid tumor can cause significant effects on the patient’s digestive system. One of the most common symptoms is difficulty swallowing, due to the tumor pressing on the esophagus. When the esophagus is compressed, the patient will find it difficult to swallow food and drinks, and may even feel pain when swallowing. This not only causes discomfort but also affects the ability to consume enough nutrients every day, leading to malnutrition and weight loss.
In addition, frequent choking and nausea may occur, reducing the patient’s quality of life. If not treated promptly, these problems can lead to more serious complications, affecting the entire digestive system and overall health.

When the esophagus is compressed, the patient will find it difficult to swallow food and drink, and may even feel pain when swallowing.
Impact on the immune system
Thyroid disease, including left lobe thyroid adenoma, can cause impaired immune system function. The thyroid gland plays an important role in producing hormones that regulate many physiological processes in the body, including the immune system. When the thyroid gland is damaged or has a tumor, hormone production can be disrupted, leading to impaired immunity. This makes the body susceptible to infections and other diseases, due to a reduced ability to fight bacteria and viruses.
In addition, thyroid hormone imbalance can also cause autoimmune reactions, in which the immune system attacks the body’s own tissues. This not only worsens the patient’s health condition but also causes many complicated complications. Therefore, proper management and treatment of left lobe thyroid adenoma is essential to maintain and improve the body’s immune function.
Preventive measures for left lobe thyroid adenoma
Maintaining a healthy diet, regular health check-ups and limiting exposure to risk factors are effective preventive measures for left lobe thyroid adenoma. A diet rich in iodine, zinc and selenium helps support thyroid function.
In addition, regular health check-ups help detect thyroid abnormalities early, thereby providing timely intervention. Limiting exposure to risk factors such as toxic chemicals, radiation and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding prolonged stress are also important measures to help reduce the risk of developing thyroid adenoma.
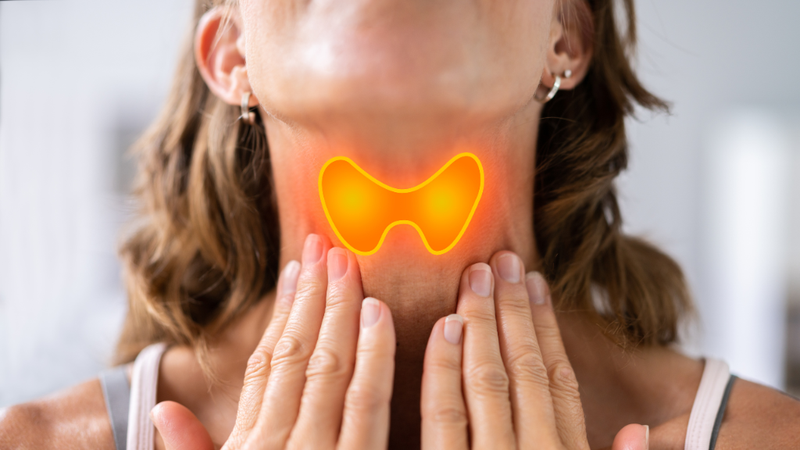
Understanding the function and pathology of the thyroid gland plays an important role in the early detection and effective treatment of left thyroid gland tumors.
Understanding the symptoms, causes and methods of diagnosing left thyroid tumors will help patients detect them early and seek timely medical intervention, thereby improving the chances of successful treatment and preventing complications. Hopefully, this article has provided readers with useful knowledge about this disease.





