Nutrition and nutritional control in daily life and treatment of related diseases are issues of concern today. Proper nutritional care is a measure to help maintain health and support effective treatment of diseases.
1. Learn about nutrition
1.1 What is nutrition?
Nutrition is the provision of essential nutrients in the form of food for cells to maintain life. Nutrition includes activities such as: Eating, drinking, absorbing, transporting and using nutrients, and excreting waste.
Nutritionists are medical professionals specializing in human nutrition, meal planning. They are trained to give advice on safe diets based on information about each individual’s health and diseases. Clinical nutritionists will focus on the role of nutrition in chronic diseases, helping to prevent and treat nutritional deficiencies before having to use drugs.
If you have a healthy, scientific diet, many health problems can be prevented or alleviated. On the contrary, a diet lacking in nutrients can lead to adverse health effects, causing malnutrition, osteoporosis, negative effects on cardiovascular disease, diabetes, etc.
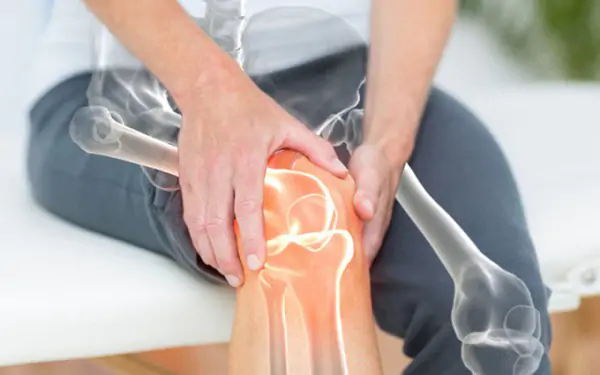
A diet lacking in nutrients can cause osteoporosis.
1.2. What are nutrients?
Nutrients are substances or chemical compounds that maintain life and body function through metabolism. For humans, nutrients are provided through daily meals. Types of nutrients include:
- Glucid (carbohydrates): Provide the main energy in meals, accounting for 60 – 70% of total energy in meals. Cereals and tubers are rich in glucid;
- Lipid (fat): Includes 2 types of fat and oil, different in chemical structure and fatty acids. Fat has a high energy density, found in foods such as animal fat (pork, chicken, fish), butter, whole milk, vegetable oil (peanut oil, sesame oil), …;
- Protein (protein): Is the basic structural component and functional component of cells in the body. Protein is found in meat, fish, eggs, milk or protein-rich nuts;
- Micronutrients: Including vitamins, minerals and trace minerals. If these substances are lacking, disease will
- occur; Fiber: Is a component of plant cell walls, which helps the body digest. Fiber is found in vegetables, tubers and fruits.

Fiber helps support the body’s digestive system.
2. What is dietetics?
Dietetics is a branch of nutrition, responsible for researching and developing formulas and diets for normal people or patients. Dietetics determines normal diets and disease diets.
Training a dietetics specialist includes:
- Equipping basic nutrition knowledge and nutrition for subjects;
- Providing knowledge and practice for examining and consulting outpatients; monitoring and evaluating the nutritional status of patients during inpatient treatment;
- Providing knowledge and practice for treating common diseases with a pathological diet;
- Providing knowledge and practice on how to organize, manage, and supervise the activities of the dietetics department at the hospital.
When receiving nutritional advice from experts, patients should absolutely comply with all instructions to effectively treat the disease and improve their quality of life.





