Currently, the rate of diabetes in our country is tending to be younger. The disease has a significant impact on health, daily life and especially causes many serious complications. So what is diabetes, is it scary? The article below will share with you all the related information. Let’s take a look!
1. What is diabetes?
After eating, carbohydrates from the meal will be converted into a type of sugar called glucose. This type of sugar is absorbed in the intestines and dissolved into the blood. At this time, the pancreas will secrete a hormone called insulin, which has the effect of bringing glucose into cells to provide energy for the body.
If the ability of insulin to function is problematic or the amount of glucose in the body increases beyond its capacity, insulin cannot respond. At that time, a certain amount of sugar will not be converted into a source of energy for the body and will be in excess in the blood. The condition of sugar levels exceeding the allowable ratio in the blood is called diabetes.
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a disorder of carbohydrate metabolism. The disease is mainly caused by the pancreas producing a lack of insulin hormone or this hormone has a reduced ability to act in the body, leading to high blood sugar levels.
This disease is one of the causes of other serious illnesses such as: kidney failure, blindness, stroke, coronary heart disease, etc.
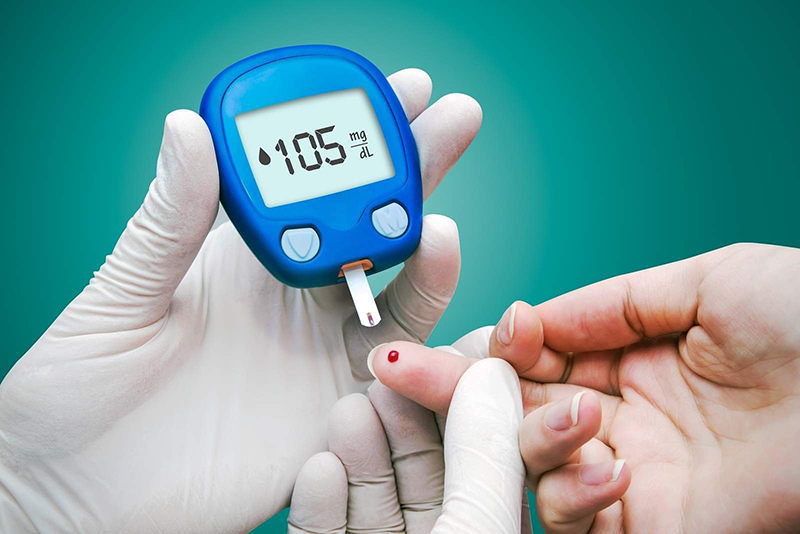
Diabetes occurs when blood sugar levels exceed the allowable rate.
2. What type of diabetes do you have?
Usually, diabetes includes 2 main types of disease:
Type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is a disease caused by abnormalities of the β cells of the islets of Langerhans, which reduce the secretion of insulin hormone or do not secrete insulin, causing danger to life. The disease mostly occurs in children and young people (under 20 years old), accounting for about 5 – 10% of the total number of people with diabetes. In this type of disease, symptoms often occur suddenly and progress rapidly, so the disease can be recognized.
Cause: The cause of type 1 diabetes is not clearly identified. Doctors believe that the cause of the disease is mainly due to genetics combined with environmental factors.
You are at high risk of the disease if your mother or brother, sister, or sibling has type 1 diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes
This is the most common type of disease, often found in people over 40 years old and is tending to be younger. The number of cases in this form accounts for about 90 – 95% of all patients with diabetes. The disease does not show functional symptoms so it is difficult to detect.
In addition to the two main types of the disease above, there is another type of the disease that only occurs in pregnant women.
Gestational diabetes
This is an abnormal condition in the process of carbohydrate metabolism. Gestational diabetes will disappear immediately after giving birth. If not treated promptly, the disease can cause negative effects, affecting the mother and baby.
Cause: In pregnant women, the placenta produces hormones to help maintain pregnancy. These hormones make the cells more resistant to insulin. When the pancreas cannot produce enough insulin to overcome this resistance, the amount of sugar accumulated in the blood increases, leading to gestational diabetes
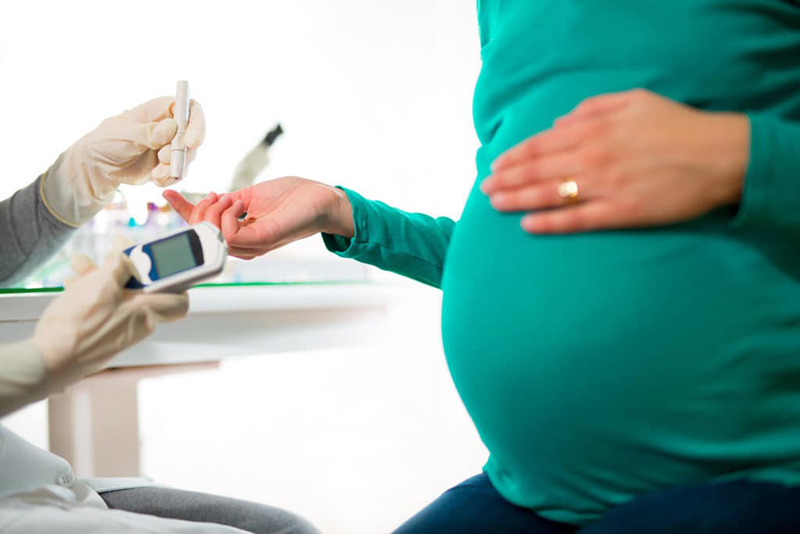

Gestational diabetes can cause complications that affect both mother and baby.
3. Symptoms of the disease
Here are some typical symptoms of the disease:
- Polyuria: High blood glucose levels lead to high glucose levels in the first urine, exceeding the absorption threshold in the kidneys. Therefore, part of the glucose is not reabsorbed in the proximal tubule, leading to the presence of sugar in the urine. At the same time, due to the high amount of sugar in the urine, it increases the osmotic pressure of the urine. Therefore, water diffuses into the urine and increases the volume of urine, causing polyuria. Children may have nocturnal enuresis due to polyuria.
- Drink a lot: When the body is dehydrated, it stimulates the hypothalamus to cause thirst, causing the patient to drink water continuously.
- Eat a lot: Because the body cannot use sugar to create energy, the patient will feel hungry quickly, stimulating them to eat a lot.
- Weight: Although eating more than usual, because the body cannot use glucose to create energy, it must increase lipid and protein degradation to compensate. Therefore, the patient is often thin and pale.
In addition, the patient also has symptoms such as: dry mouth, nausea, blurred vision, slow healing of ulcers, etc. To know for sure whether you have the disease or not, you should see a doctor and do tests.
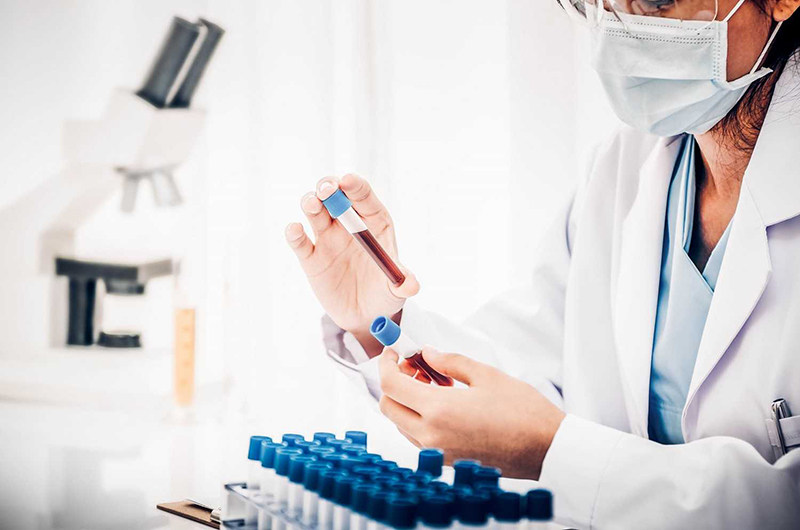

You should have tests done to know for sure if you have diabetes or not.
4. Possible complications
The longer a person has diabetes, the more difficult it is to control blood sugar levels. At this time, the risk of complications increases, they develop gradually, and if severe, can be life-threatening.
Some complications that can occur in patients are:
- Cardiovascular disease: When you have diabetes, you are at higher risk of cardiovascular diseases such as heart attack, atherosclerosis, stroke, etc. than normal.
- Nerve damage: Excess sugar in the blood damages the small blood vessels that nourish the nerves, especially in the legs. Therefore, patients often feel itching, numbness or pain in the fingertips or toes and it spreads more and more. If left untreated, the patient may lose sensation. In addition, when the nerves are damaged in the digestive system, it can also cause vomiting, diarrhea or constipation.
- Kidney damage: Diabetes can cause serious damage to kidney tissue. In severe cases, the patient may have kidney failure or end-stage kidney disease requiring dialysis.
- Eye damage: When suffering from this disease, the blood vessels of the retina can be damaged and there is a possibility of other serious vision problems: cataracts, glaucoma, etc.
- Alzheimer’s disease: People with type 2 diabetes are at high risk of Alzheimer’s disease.
Complications that can occur during pregnancy:
The mother may suffer from preeclampsia with symptoms such as: high blood pressure, excess protein in the urine, swollen legs. Not only that, pregnant women are also at risk of this disease in the next pregnancy, and when they get older, they can develop diabetes, typically type 2 diabetes.
The fetus can develop faster than its age, with a risk of type 2 diabetes in the future. If the pregnant mother does not treat it, the child may die before or after birth.
5. Diabetes treatment
When you find out you have diabetes, you need to see a doctor for examination and timely treatment to avoid dangerous complications. If you have type 1 diabetes, your body does not produce insulin, so you need to use it for the rest of your life. If you have type 2 diabetes, you need to pay special attention to your diet and exercise regularly. At the same time, you can also use oral or injectable insulin, metformin to control blood sugar levels.
To prevent the disease from getting worse, patients should eat foods with low sugar content, eat lots of green vegetables, divide meals into small portions, and exercise regularly.
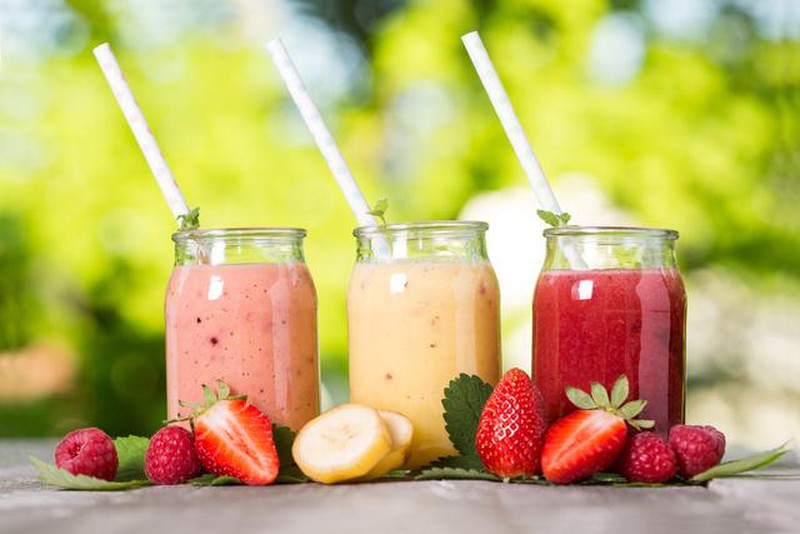

Patients should eat lots of green vegetables and drink lots of fruit juice.
When you have diabetes, you should limit your intake of the following foods:
- Red meat, animal organs, egg yolks, etc.
- Sweet cakes, candies, carbonated soft drinks, milk, beer and alcoholic beverages.
- Starch: rice, noodles, pho, etc.
Diabetes can leave many dangerous complications. Therefore, if you suspect you have this disease, you should see a doctor for examination and timely treatment. In addition, a reasonable, scientific diet and regular exercise will help you have good health and help prevent disease better.





