Manganese is an essential mineral nutrient that is important for a number of functions in our body, but not everyone knows about it. The article below will help you understand what manganese is and the role of manganese in the body.
Although trace elements only need to be supplemented in small amounts in each meal, they play a very important role in your health, one of which is manganese – a substance that is essential for many of our daily activities. Let’s find out what manganese is, the role of manganese in the body and foods rich in manganese.
1. What is manganese?
Manganese is a trace element essential for the body’s vital activities.
Manganese is a naturally occurring element and an essential mineral nutrient required by the body in small amounts.
Manganese functions primarily as a coenzyme in a number of biological processes such as macronutrient metabolism, bone formation, ammonia clearance, and neurotransmitter synthesis. It is an important component of dozens of proteins and enzymes, and is found in all tissues.
Although essential for life, excess manganese is toxic. Therefore, maintaining appropriate intracellular manganese levels is important.
2. The role of manganese
Manganese helps strengthen bones
Manganese helps support bone mineral density
Manganese is essential for bone health, including bone growth and maintenance
Studies on osteoporosis risk factors have shown that approximately 50% of postmenopausal women and 25% of men aged 50 and older will experience a fracture due to osteoporosis.
When combined with the nutrients calcium, zinc, and copper , manganese supports bone mineral density. This is especially important in older adults.
However, other studies on the effects of calcium and vitamin D supplementation on bone mineral density have shown that supplements containing only calcium and vitamin D have similar effects. Therefore, the role of manganese in bone health is still being studied.
Manganese helps reduce inflammation and reduce the risk of disease

Manganese is important in the formation and function of antioxidants.
Manganese is part of the antioxidant enzyme superoxide dismutase (SOD), which is considered one of the most important antioxidants in the body.
SOD specifically helps counteract the negative effects of free radicals, which are molecules that can cause damage to cells in the body, contributing to aging, heart disease, and some cancers, by converting superoxide, one of the most dangerous free radicals, into smaller molecules that do not damage the body’s cells.
Therefore, researchers suggest that adequate intake of antioxidant nutrients such as manganese may reduce the production of free radicals and improve antioxidant status in people with the disease
In addition, research has shown that SOD may be useful as a therapeutic agent for inflammatory disorders.
Combining manganese with glucosamine and chondroitin may reduce joint pain caused by inflammation of the lining of the joints. However, this therapy is only effective for people with mild osteoarthritis.
Manganese helps regulate blood sugar levels
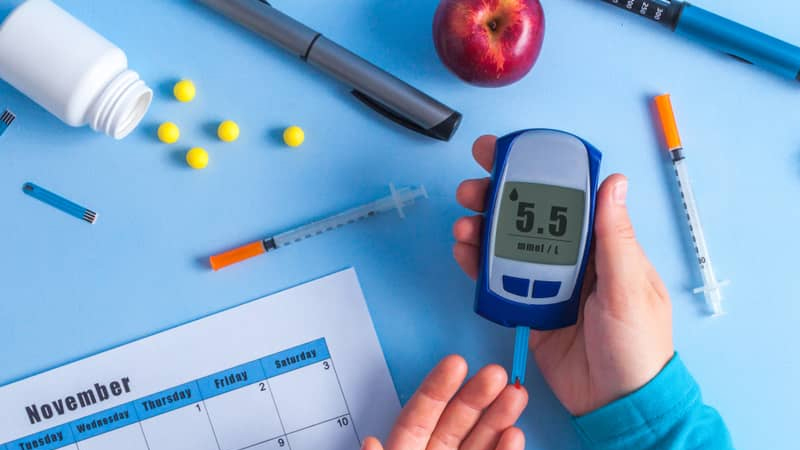

Manganese helps stabilize blood sugar levels
Manganese appears to play a role in regulating blood sugar levels.
A study of trace element levels in the blood of diabetic patients found that people with diabetes had lower than normal levels of manganese in their blood and lower levels of the antioxidant enzyme manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD).
In addition, manganese is concentrated in the pancreas. It is involved in the production of insulin, which removes sugar from the blood. Therefore, manganese may contribute to proper insulin secretion and help stabilize blood sugar levels.
However, researchers are still trying to determine whether low manganese levels contribute to the development of diabetes or whether diabetes causes manganese levels to drop.
Manganese promotes brain health and reduces the risk of stroke

Manganese reduces the risk of stroke and epilepsy
Manganese is essential for healthy brain function and is often used to help treat neurological disorders.
Manganese’s antioxidant properties help protect against free radicals that can damage brain cells in the nerve pathways.
Manganese can also bind to neurotransmitters and stimulate faster or more efficient movement of electrical impulses throughout the body, which can improve brain function.
Manganese is also known as a vasodilator, which helps widen veins to efficiently deliver blood to tissues such as the brain. Adequate levels of manganese in the body can help increase blood flow and reduce the risk of certain health conditions such as stroke and epilepsy.
Manganese increases the body’s metabolism

Manganese plays an important role in the metabolism of nutrients.
Manganese activates many enzymes in metabolism, helping with digestion, protein and amino acid utilization, and cholesterol and carbohydrate metabolism.
In addition, it acts as a cofactor in growth, reproduction, energy production, immune response, brain regulation, and is involved in a variety of chemical processes in the body.
Manganese may reduce symptoms of premenstrual syndrome (PMS)

Manganese reduces painful symptoms during menstruation
When combined with calcium, manganese can act as a natural remedy to reduce premenstrual symptoms including anxiety, cramps, pain, mood swings and even depression.
An analysis of the effects of dietary calcium and manganese on menstrual symptoms in 10 women found that those with low blood levels of manganese experienced more pain and mood-related symptoms during their premenstrual period regardless of calcium intake.
Manganese plays an important role in thyroid function
Manganese is essential for the production of thyroxine and the health and normal functioning of the thyroid gland.
Manganese plays a role in the production of thyroxine, a hormone important for normal thyroid function, which helps the body maintain appetite, metabolism, weight, and increases the efficiency of other organs.
Manganese deficiency can cause or contribute to hypothyroidism, which can lead to weight gain and hormonal imbalances.
Manganese helps heal wounds
Manganese helps wound healing by forming collagen in skin cells
Trace minerals, such as manganese, are important in wound healing.
Manganese is needed to produce the amino acid proline, which is essential for collagen formation and wound healing in human skin cells.
Observational studies of wound healing have shown that applying creams containing manganese, calcium, and zinc to chronic wounds for 12 weeks can improve healing.
3. Foods rich in manganese
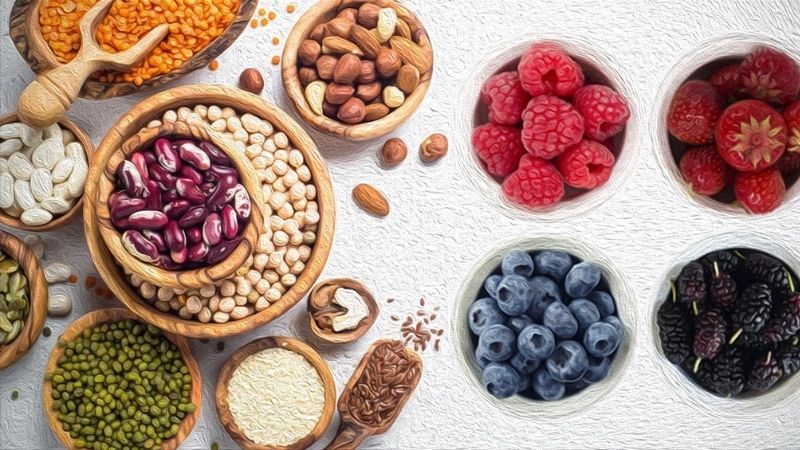

Manganese is found naturally in many foods.
Like any other nutrient, manganese is important for health, getting enough manganese will ensure the body is always healthy. In addition to supplementing manganese with appropriate medications and vitamins when needed, through daily meals, foods also help the body supplement manganese safely.
Foods rich in manganese include the following: oats, wheat, soybeans, green beans, chickpeas, garlic, brown rice, pineapple, tofu, raspberries, corn, green turnips, bananas, strawberries
Note that foods or iron supplements that reduce the absorption of manganese, phosphorus and calcium can also reduce the ability to retain manganese, but in lower amounts than iron.
Adequate manganese supplementation is important for overall health, but should not be taken in more than necessary, as it is considered a heavy metal and excessive consumption can be dangerous.
Hopefully the above article has helped you understand what manganese is and the important role of manganese in the body’s vital activities. Supplement manganese with daily foods to protect the health of yourself and your family!





