Stroke is an extremely dangerous disease, the mortality rate is extremely high if not treated promptly. Previously, the disease was common in middle-aged or elderly people. However, there is now a trend of rejuvenation, people in their 20s – 30s are also susceptible to this dangerous disease.
1. What is a stroke and how dangerous is it?
A stroke is a clinical syndrome characterized by an acute loss of brain function (usually localized), lasting more than 24 hours or leading to death within 24 hours. Localized neurological symptoms are consistent with the area of the brain distributed by the damaged artery, not due to trauma. Therefore, the disease is also called “cerebrovascular accident”.
From the time a patient has a stroke, if there is only a lack of oxygen for 4-5 minutes, the damage is irreversible. This affects the ability to think and function of the body in the future, and in the worst case, if not treated promptly, the patient will die.
Almost all people who are cured have sequelae such as paralysis, emotional disorders, aphasia, visual impairment, etc.
The disease is divided into 2 types as follows:
Ischemic stroke
The rate of this disease due to ischemia is quite high, over 85% of all cases.
Causes:
– Blood clot.
– Embolism.
– Vasospasm.
– Cerebral hemorrhage
Thin or weak artery walls lead to cracks or leaks, making blood vessels prone to rupture. The main causes are:
– High blood pressure.
– Rupture of a cerebral aneurysm.
– Arteriovenous malformation.
– Blood clotting disorder.
– Bleeding in the cerebral infarction.
– Bleeding of unknown cause.
In addition, there are many cases of “transient cerebral ischemia”, which means that blood flow to the brain is temporarily stopped. The patient will be sick for a short period of time, this is a warning sign of future risks that need close attention.
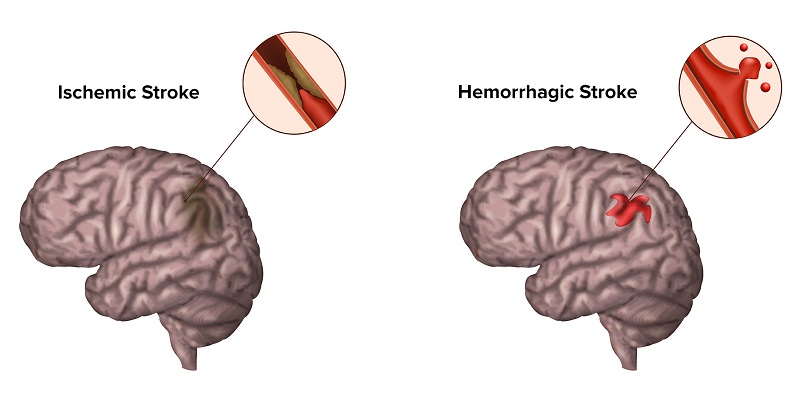
Images of two types of stroke
2. Causes of stroke
2.1. Objective causes
– Age: Elderly people are more likely to have a stroke, from the age of 55 onwards, the risk of the disease doubles every 10 years.
– Race: White people are 2 times less likely to have the disease than African Americans.
– Gender: The rate of disease in women is usually lower than in men.
– Family history: If someone in the family has had this disease, the risk of getting this disease is higher than that of normal people.

Older people have a higher rate of this disease than younger people.
2.2. Due to the influence of disease
The following diseases are also risk factors leading to stroke.
Diabetes
Diseases related to diabetes are also the cause of increased risk of this disease.
High blood pressure
Patients with high blood pressure create conditions for blood clots to form and put pressure on the artery walls, making them susceptible to rupture. This is the first step leading to ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic stroke.

Hypertensive patients need to pay close attention to their health.
Cardiovascular disease
People with cardiovascular disease are at higher risk of developing the disease than normal people.
Hyperlipidemia
Patients with hyperlipidemia have high levels of cholesterol, which can accumulate on the walls of arteries, thereby causing blockage of blood vessels in the brain.
Obesity
People who are obese are at high risk of cardiovascular disease, high blood pressure, hyperlipidemia, and stroke.
Stroke
People who have had a stroke or transient ischemic attack (described in section 1) are at high risk of developing this disease in the future. Within a few months after the disease, the possibility of recurrence is very high, patients should pay attention. The high risk of recurrence is about 5 years, after this period of time the risk will gradually decrease but should not be subjective.
Unhealthy lifestyle
Smoking also increases the risk of disease by 2 times, not only that, it also affects many other organs in the body.
Improper diet, unreasonable exercise regimen, lack of exercise, etc. are all causes that increase the risk of this dangerous disease.
3. Signs of stroke
Depending on each person’s physical condition, the signs of the disease are also different, these signs can appear and pass very quickly, making the patient subjective or can also be repeated many times.
Some manifestations of the disease are as follows:
– The face is half or completely numb, the smile is distorted, the body suddenly loses strength, and is often tired.
– The body shows signs of paralysis or difficulty moving, and the inability to lift both arms above the head at the same time is the clearest sign of the disease.
– Having problems speaking such as sticking words, unclear words, slurred speech.
– Dizziness, sudden loss of balance, decreased vision.
– Headaches may or may not be accompanied by nausea, the headache comes suddenly.

Dizziness, sudden loss of balance, and decreased vision are signs of the disease.
When you notice yourself having the above signs, you should proactively go to a specialist as soon as possible. Early detection of the disease and timely intervention measures help us avoid serious consequences.





